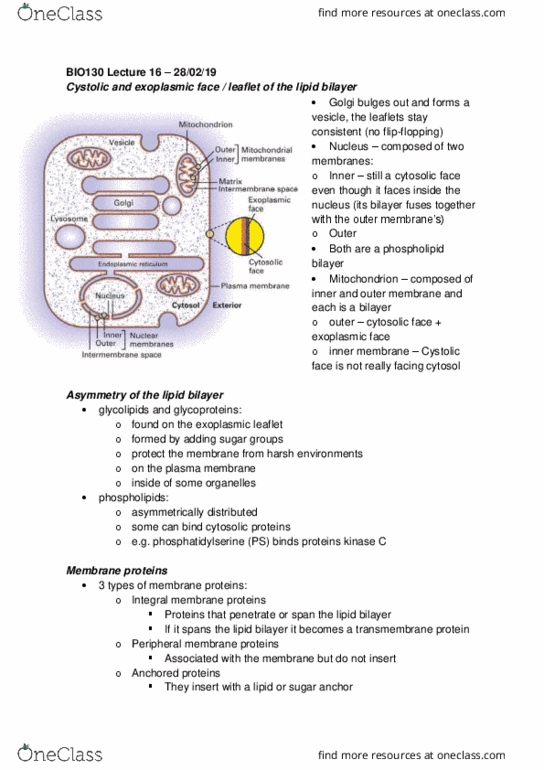
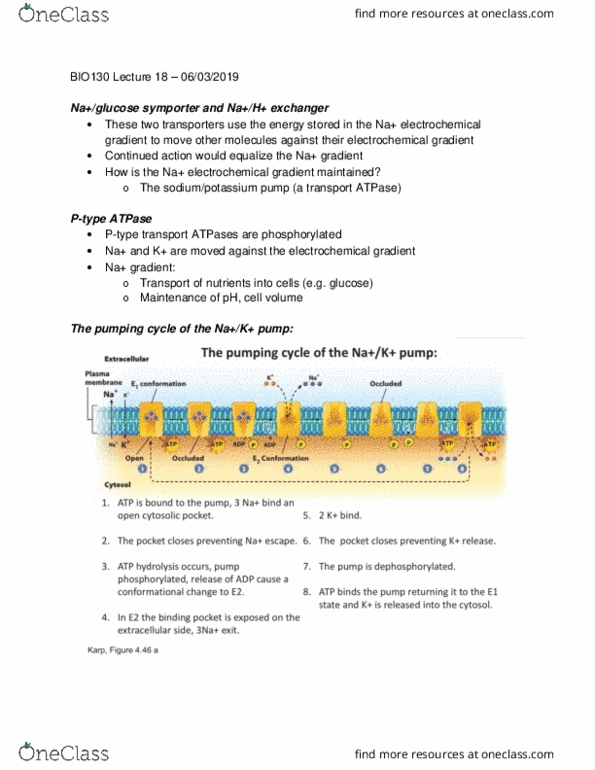
BIO130H1 Lecture Notes - Lecture 17: Resting Potential, Electrochemical Gradient, Passive Transport
BIO130H1 verified notes
17/26View all
Document Summary
Proteins involved in membrane transport: multipass transmembrane proteins, create a protein-lined path across cell membrane, transport polar and charged molecules. Ions, sugars, amino acids, nucleotides, various cell metabolites: each transport protein is selective, transport specific class of molecules, different cell membranes, have different complement of transport proteins. Channel proteins: hydrophilic pore across membrane, most channel proteins are selective. Ion channels transport a specific ion: passive transport, weak interactions with solute, faster transport by channel than transporter, several molecules pas through when open. Ion channels: found in animals, pants, microorganisms, two types, non-gated always open, k+ leak channels. Major role in generation of resting membrane potential in animal cells: always open, k+ moves out of cell. Important in the plasma membrane of animal cells. Transporter proteins: bind a specific solute, go through a conformational change that transports that solute across the membrane, transport proteins interact a lot and bind strongly.