BIO130H1 Lecture Notes - Lecture 16: Cytosol, Lipid Bilayer, X-Ray Crystallography
179 views3 pages
Verified Note
2 Mar 2019
School
Department
Course
Professor
BIO130H1 verified notes
16/26View all
Document Summary
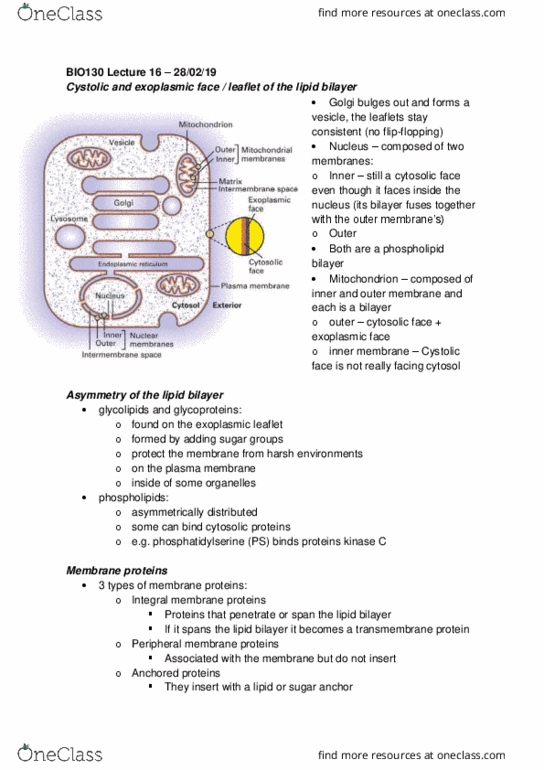
Cystolic and exoplasmic face / leaflet of the lipid bilayer: golgi bulges out and forms a vesicle, the leaflets stay consistent (no flip-flopping, nucleus composed of two membranes: Membrane proteins: 3 types of membrane proteins: Integral membrane proteins: proteins that penetrate or span the lipid bilayer. Ion channels: conformational changes regulate permeability, beta-barrel, some channels in bacteria, mitochondria, chloroplasts, rigid, do not undergo conformational changes. Techniques: how are these structures identified: x-ray crystallography, determines 3d structure, hydrophobicity plots, segments of 20-30 hydrophobic aas can span the lipid bilayer as an -helix. Lipid-anchored membrane proteins: gpi anchor, synthesis in er lumen, end up on cell surface, other lipid anchors (fatty acid, penyl, cytosolic enzymes add the anchor, directs protein to the cytosolic face. Peripheral membrane proteins: bound to other proteins or lipids on either face of the membrane by non- covalent interactions. Techniques: extraction membrane proteins: peripheral membrane proteins use gentle extraction that does not destroy lipid bilayer.