chloe
Queen Mary, University of London
13 Followers
0 Following
13 Helped
Let's learn together!!
chloeLv10
14 Sep 2022
Answer: answer is :availability of close substitutes.
chloeLv10
14 Sep 2022
Answer: answer is input prices.
chloeLv10
14 Sep 2022
Answer: answer is f
chloeLv10
14 Sep 2022
Answer: answer is supply, shifts to the right, a decrease, an increase
chloeLv10
14 Sep 2022
Answer: answer is c
chloeLv10
14 Sep 2022
Answer: answer is (ii) the labor force;
chloeLv10
14 Sep 2022
Answer: answer is b
chloeLv10
14 Sep 2022
Answer: answer is b false
chloeLv10
14 Sep 2022
Answer: the answer is d
chloeLv10
14 Sep 2022
Answer: the answer is d
chloeLv10
13 Sep 2022
Answer: answer is C
chloeLv10
13 Sep 2022
Answer: answer is D
chloeLv10
13 Sep 2022
Answer: answer is D
chloeLv10
13 Sep 2022
Answer: answer is Endocytosis, exocytosis
chloeLv10
13 Sep 2022
Answer: answer is b
chloeLv10
13 Sep 2022
Answer: answer is D
chloeLv10
13 Sep 2022
Answer: answer is A
chloeLv10
13 Sep 2022
Answer: answer is C
chloeLv10
13 Sep 2022
Answer: answer is A
chloeLv10
13 Sep 2022
Answer: answer is : C
chloeLv10
13 Sep 2022
Answer: answer is Option 4
chloeLv10
13 Sep 2022
Answer: answer is C
chloeLv10
13 Sep 2022
Answer: answer is C
chloeLv10
13 Sep 2022
Answer: answer is 4
chloeLv10
13 Sep 2022
Answer: answer is C
chloeLv10
13 Sep 2022
Answer: answer is B
chloeLv10
13 Sep 2022
Answer: answer is B
chloeLv10
13 Sep 2022
Answer: answer is C
chloeLv10
13 Sep 2022
Answer: answer is A
chloeLv10
13 Sep 2022
Answer: answer is C
chloeLv10
13 Sep 2022
Answer: answer is A
chloeLv10
13 Sep 2022
Answer: answer is A
chloeLv10
13 Sep 2022
Answer: answer is b)complex process that is difficult to define
chloeLv10
13 Sep 2022
Answer: answer is ostich
chloeLv10
13 Sep 2022
Answer: answer is R horizon
chloeLv10
13 Sep 2022
Answer: answer is C). a critical life event
chloeLv10
13 Sep 2022
Answer: answer is i x (i + j + k) = k - j
chloeLv10
13 Sep 2022
Answer: answer is 1. 21.88 % 2. 25.93 % 3. 31.97 % 4. 41.18 %
chloeLv10
13 Sep 2022
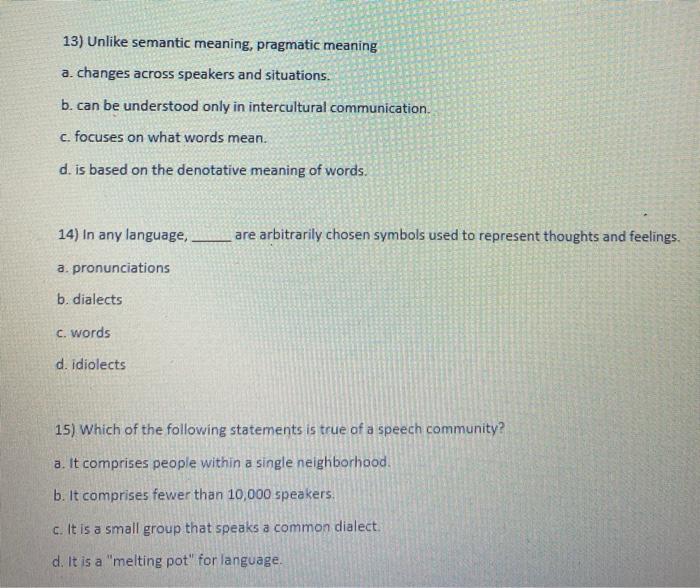
Answer: answer is 13. a 14. c 15. c
chloeLv10
13 Sep 2022
Answer: answer is (a) 480 N (b) 3.76 m/s2