CHEM 101 Lecture Notes - Lecture 17: Molecular Orbital Theory, Vsepr Theory, Lewis Structure
CHEM 101 verified notes
17/40View all
Document Summary
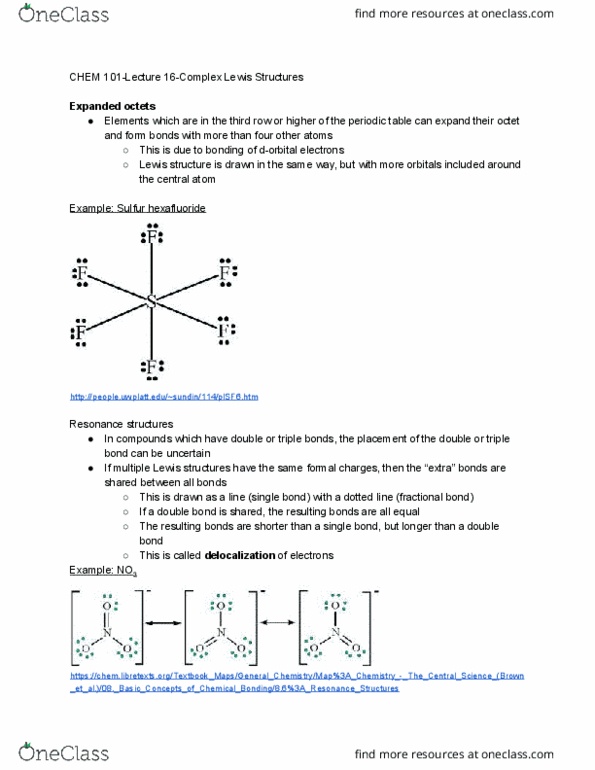
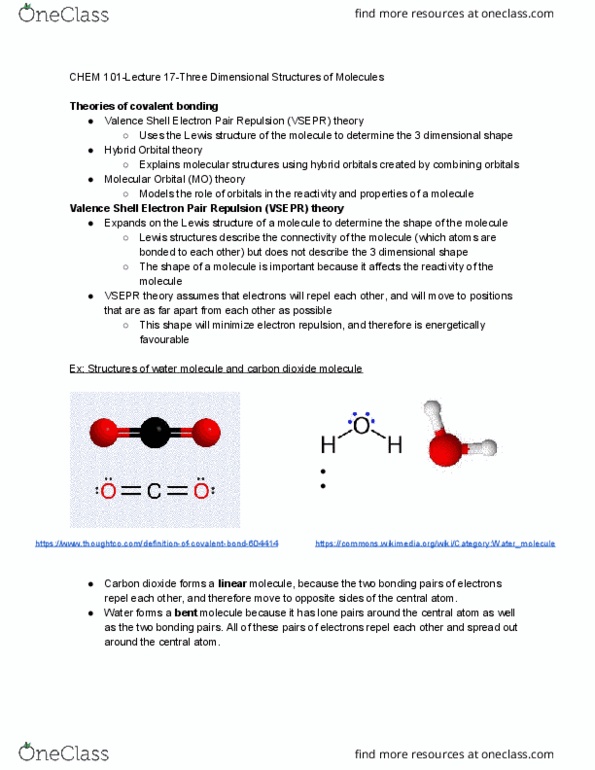
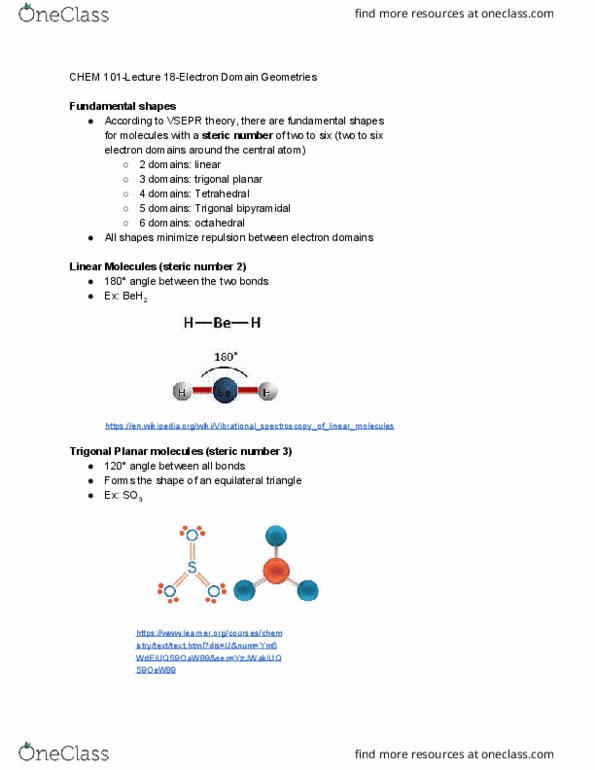
Valence shell electron pair repulsion (vsepr) theory. Uses the lewis structure of the molecule to determine the 3 dimensional shape. Explains molecular structures using hybrid orbitals created by combining orbitals. Models the role of orbitals in the reactivity and properties of a molecule. Expands on the lewis structure of a molecule to determine the shape of the molecule. Lewis structures describe the connectivity of the molecule (which atoms are bonded to each other) but does not describe the 3 dimensional shape. The shape of a molecule is important because it affects the reactivity of the molecule. Vsepr theory assumes that electrons will repel each other, and will move to positions that are as far apart from each other as possible. This shape will minimize electron repulsion, and therefore is energetically favourable. Ex: structures of water molecule and carbon dioxide molecule https://www. thoughtco. com/definition-of-covalent-bond-604414 https://commons. wikimedia. org/wiki/category:water_molecule. Water forms a bent repel each other, and therefore move to opposite sides of the central atom.