BIO230H1 Lecture Notes - Lecture 6: Golgi Apparatus, Glycosylation, Transmembrane Protein
BIO230H1 verified notes
6/13View all
Document Summary
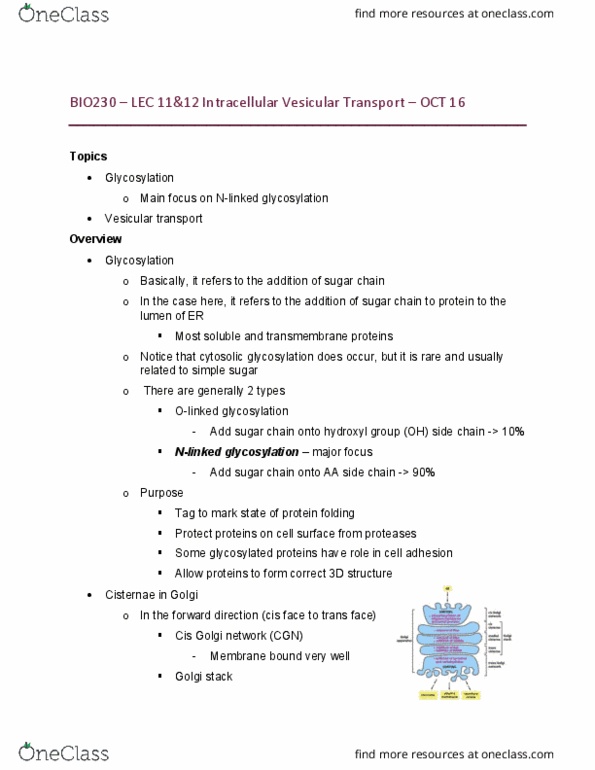
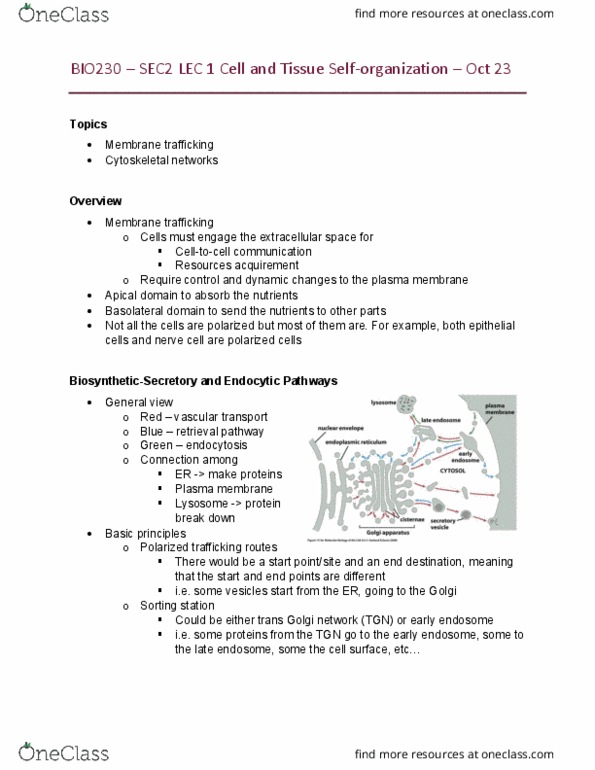
Bio230 lec 11&12 intracellular vesicular transport oct 16. Topics: glycosylation, main focus on n-linked glycosylation, vesicular transport. Overview: glycosylation, basically, it refers to the addition of sugar chain. There are generally 2 types: o-linked glycosylation. Add sugar chain onto hydroxyl group (oh) side chain -> 10: n-linked glycosylation major focus. In the forward direction (cis face to trans face: cis golgi network (cgn) Membrane bound very well: golgi stack. Gtpase would then be inactivated since it"s now bound to gdp: gef (guanine nucleotide exchange factor, exchange gdp with gtp (-> release gdp and bind gtp) 3 glucose and 1 mannose would be removed one at a time. If the protein is normally folded, it would exit from er. If the protein is still not folded, then the glycosylated transferase would recognize it and chop off the udp bound glucose, adding the glucose to the protein.