BCH210H1 Lecture Notes - Lecture 5: Zwitterion, Optical Rotation, Alpha And Beta Carbon
BCH210H1 verified notes
5/39View all
Document Summary
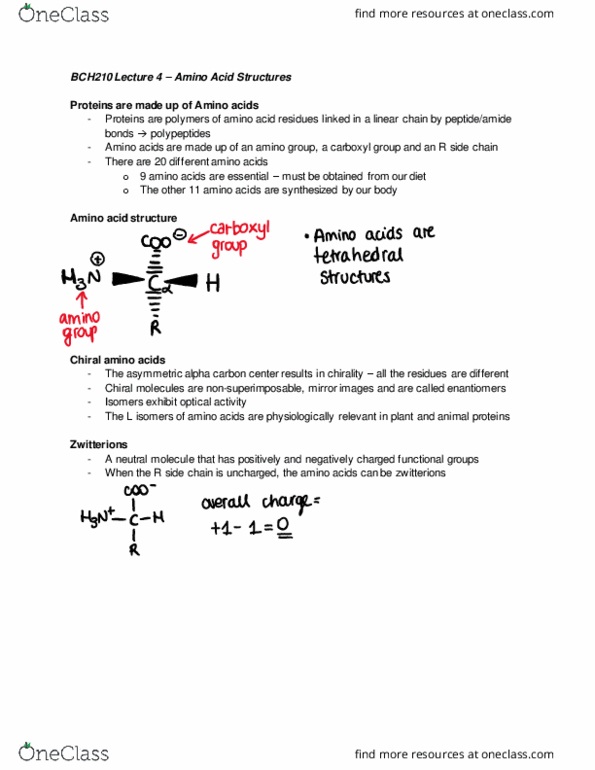
Proteins are polymers of amino acid residues linked in a linear chain by peptide/amide bonds polypeptides. Amino acids are made up of an amino group, a carboxyl group and an r side chain. There are 20 different amino acids: 9 amino acids are essential must be obtained from our diet, the other 11 amino acids are synthesized by our body. The asymmetric alpha carbon center results in chirality all the residues are different. Chiral molecules are non-superimposable, mirror images and are called enantiomers. The l isomers of amino acids are physiologically relevant in plant and animal proteins. A neutral molecule that has positively and negatively charged functional groups. When the r side chain is uncharged, the amino acids can be zwitterions. The sequence of a protein is determined by codons. All proteins being with a methionine which gets lost once the protein matures. Combine via peptide bonds to peptide bonds to form polypeptide proteins.