CHEM 1A Lecture Notes - Lecture 31: Sigma Bond, Atomic Orbital, Pi Bond
CHEM 1A verified notes
31/31View all
Document Summary
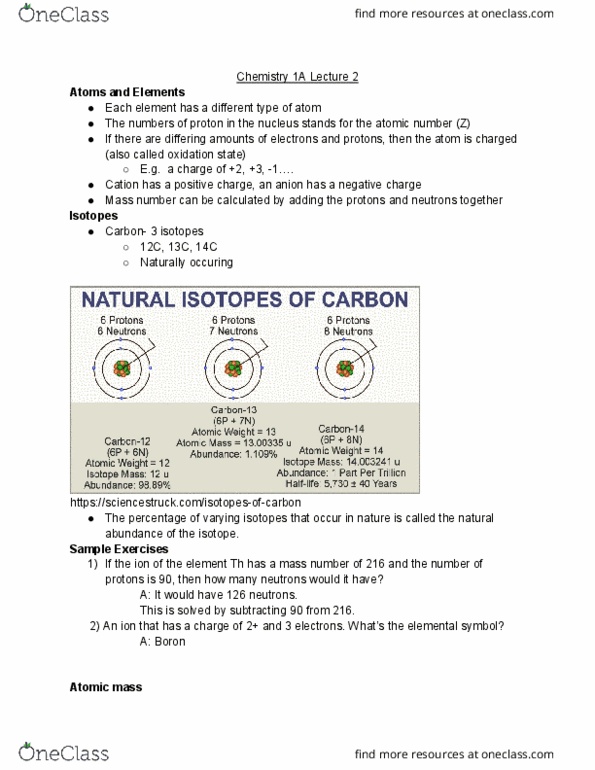
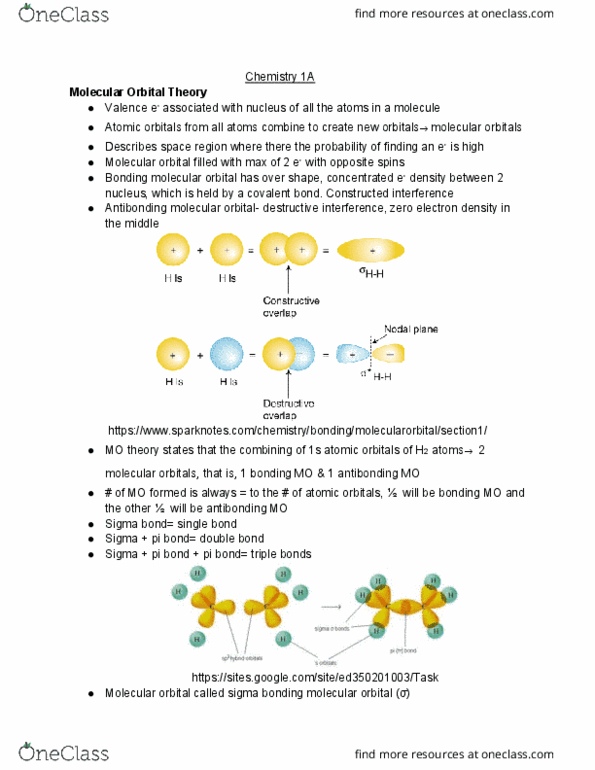
Valence e- associated with nucleus of all the atoms in a molecule. Atomic orbitals from all atoms combine to create new orbitals molecular orbitals. Describes space region where there the probability of finding an e- is high. Molecular orbital filled with max of 2 e- with opposite spins. Bonding molecular orbital has over shape, concentrated e- density between 2 nucleus, which is held by a covalent bond. Antibonding molecular orbital- destructive interference, zero electron density in the middle https://www. sparknotes. com/chemistry/bonding/molecularorbital/section1/ Mo theory states that the combining of 1s atomic orbitals of h2 atoms 2 molecular orbitals, that is, 1 bonding mo & 1 antibonding mo. # of mo formed is always = to the # of atomic orbitals, will be bonding mo and the other will be antibonding mo. Sigma + pi bond + pi bond= triple bonds. Molecular orbital called sigma bonding molecular orbital ( ) https://sites. google. com/site/ed350201003/task. Antibonding molecular orbital called sigma star ( *) antibonding molecular orbital.