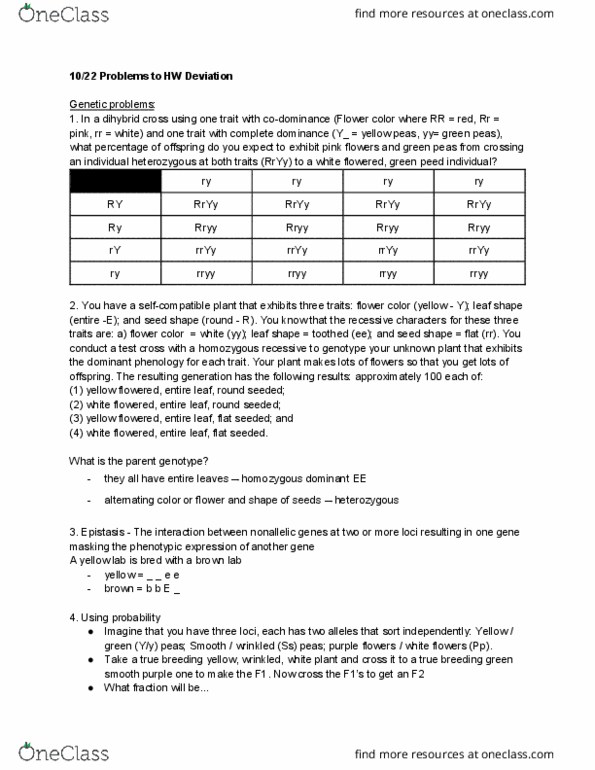
BIS 2B Lecture Notes - Lecture 11: Allele Frequency, Quantitative Genetics, Probability Distribution
Document Summary
Get access


Related Documents
Related Questions
Question 1
What would be the dimensions of a Punnett square for the cross Hh x hh?
| 4 x 4 | ||
| 2 x 2 | ||
| 2 x 1 | ||
| 1 x 1 |
Question 2
In dogs, the gene for fur color has two alleles. The dominant allele (G) codes for grey and the recessive allele (g) codes for black fur. The female dog is heterozygous. The male dog is homozygous recessive. Figure out the phenotypes and genotypes possible in their puppies by using a Punnett Square. (provide answers on one line with commas between - xx, xx, xx, xx)
Genotypes: , ,
Phenotypes: ,
Question 3
The fundamental Mendelian process which involves the separation of alleles located at the same spot on the chromosome would be called ___.
| segregation | ||
| independent assortment | ||
| continuous variation | ||
| discontinuous variation |
Question 4
Using the information given on dominant and recessive traits, state the phenotype for each genotype. Purple flowers are dominant to white flowers in pea plants.
|
|
Question 5
In dogs, the gene for fur color has two alleles. The dominant allele (G) codes for grey and the recessive allele (g) codes for black fur. The female dog has black fur and the male dog is homozygous dominant. Make a Punnett square to determine the chance of getting each genotype and phenotype below.
|
|
Question 6
Using the information given on dominant and recessive traits, state the phenotype for each genotype. Round seeds are dominant to wrinkled seeds in pea plants.
|
|
Question 7
Using the information given on dominant and recessive traits, state the phenotype for each genotype. Hairy knuckles are dominant to non-hairy knuckles in humans.
|
|
Question 8
An allele is ___.
| one of the bases in DNA | ||
| an alternate form of a gene | ||
| another term for epistasis | ||
| present only in males and is responsible for sex determination |
Question 9
In a cross of a round hybrid pea with a true breeding round parent (Rr x RR), what genotypic proportions would be observed in the offspring?
| Half heterozygous, half homozygous dominant | ||
| Half round, half wrinkled | ||
| All heterozygous | ||
| All round |
Question 10
What would be the dimensions of a Punnett Square depicting a dihybrid cross?
| 1 x 4 | ||
| 2 x 4 | ||
| 4 x 4 | ||
| 2 x 2 |