01:220:102 Lecture Notes - Lecture 19: Oligopoly, Marginal Cost, Product Differentiation
01:220:102 verified notes
19/27View all
Document Summary
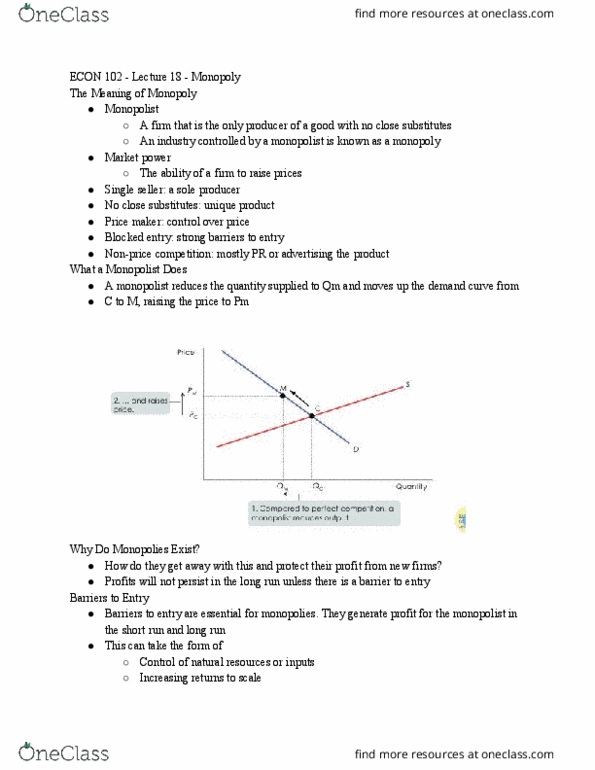
Monopolies are not permanently protected from forces of entry and imitation. The main difference between a competitive firm and a monopoly is the length of time that a firm can earn above average profits. Monopolists can earn positive profits in the long run. Barriers to entry: can maintain positive long run profits. Firms will price at the point where (p-mc)/p = 1/e. In the long run the forces of entry and imitation (the development of close substitutes) make the monopolists curve more elastic. The elastic demand will push price down toward marginal cost and will eventually drive economic profits to zero. A few large firms with a high level of output. Oligopoly market structures are characterized by only a few firms, each of which is large relative to the total industry. Typical number of firms is between 2 and 10. An oligopoly market composed of two firms is called a duopoly.