CAS EC 101 Lecture Notes - Lecture 16: Budget Constraint, Consumer Choice, Normal Good
CAS EC 101 verified notes
16/41View all
Document Summary
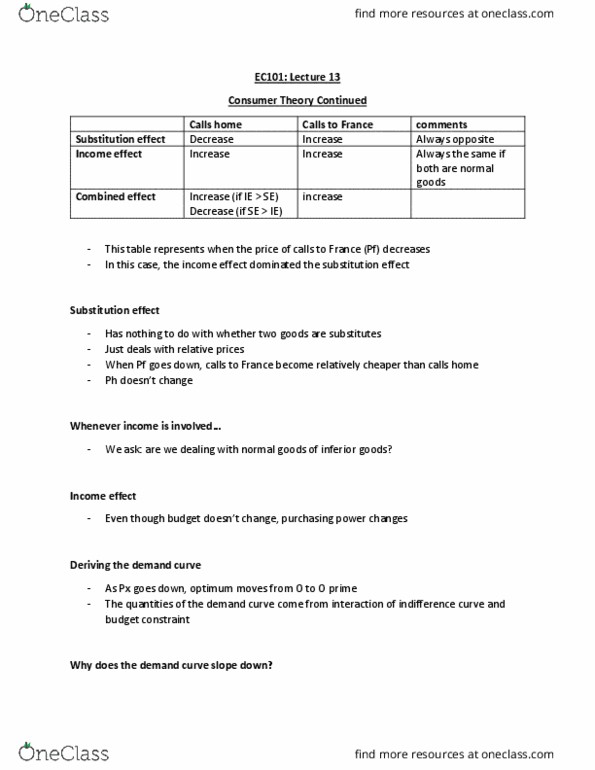
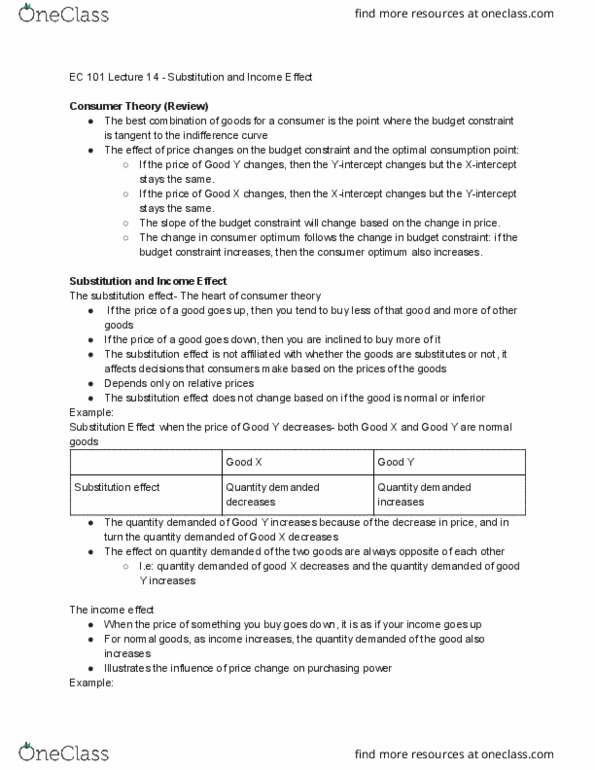
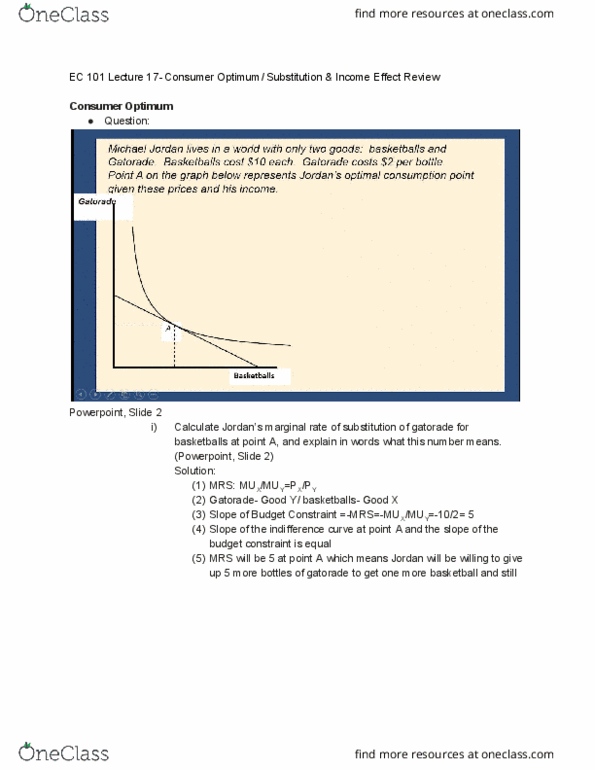
Ec 101 lecture 14 - substitution and income effect. The best combination of goods for a consumer is the point where the budget constraint is tangent to the indifference curve. The effect of price changes on the budget constraint and the optimal consumption point: If the price of good y changes, then the y-intercept changes but the x-intercept stays the same. If the price of good x changes, then the x-intercept changes but the y-intercept stays the same. The slope of the budget constraint will change based on the change in price. The change in consumer optimum follows the change in budget constraint: if the budget constraint increases, then the consumer optimum also increases. The substitution effect- the heart of consumer theory. If the price of a good goes up, then you tend to buy less of that good and more of other goods.