Mathematics 1229A/B Lecture Notes - Lecture 1: Parallelogram Law, Parallelogram
MATH 1229A/B verified notes
1/5View all
Document Summary
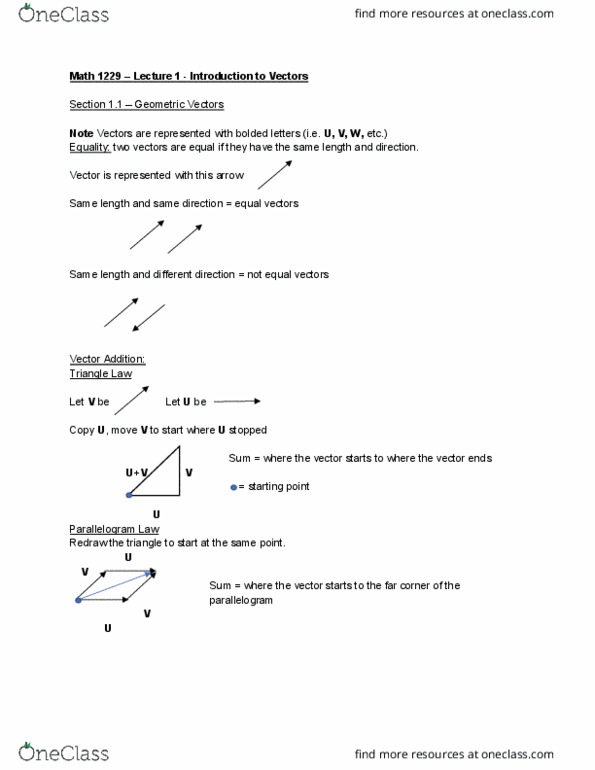
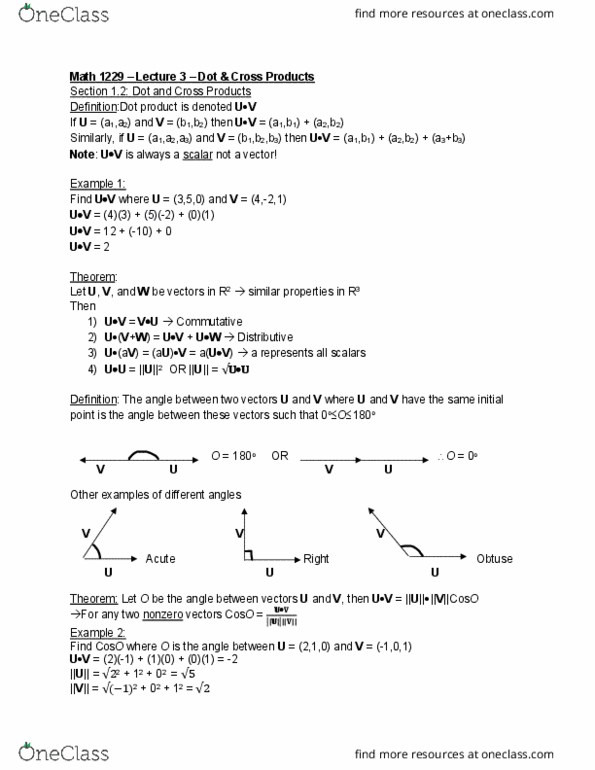
Math 1229 lecture 1 - introduction to vectors. Note vectors are represented with bolded letters (i. e. u, v, w, etc. ) Equality: two vectors are equal if they have the same length and direction. Same length and same direction = equal vectors. Same length and different direction = not equal vectors. Copy u, move v to start where u stopped. Redraw the triangle to start at the same point. Sum = where the vector starts to where the vector ends. Sum = where the vector starts to the far corner of the parallelogram. Vectors that are scalar multiples are parallel (colinear) on the same line. A vector in 2-space is an ordered pair (a,b) of real numbers. A vector in 3-space is an ordered triple (a,b,c) of real numbers. Equality in 3-space: two vectors are equal if their corresponding components are equal. Scalar multiplication: multiply each component by the scalar. Subtraction: u v = u + (-1)v.