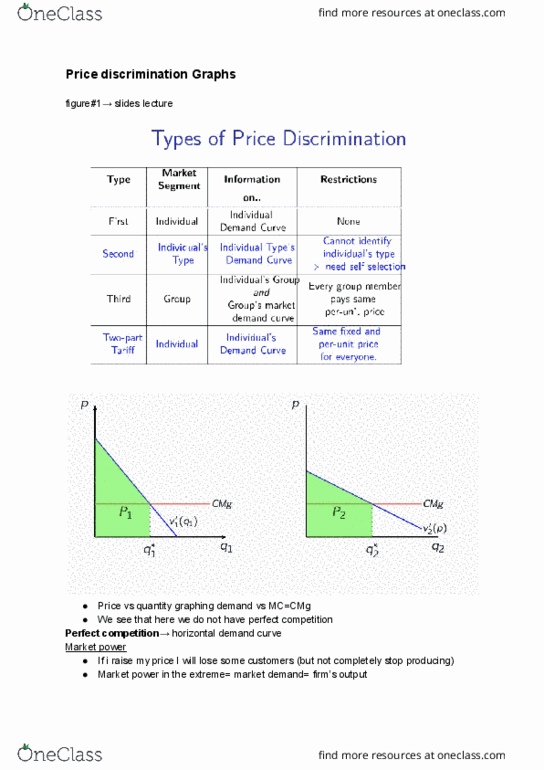
ECO200Y1 Lecture Notes - Lecture 12: Gross Fixed Capital Formation, Fixed Capital, Capital Formation
ECO200Y1 verified notes
12/26View all
Document Summary
Investment, in macroeconomics, is the expenditure on goods and services that will be used in the future in the production of other goods and services. Also called training gross capital, investment increases the productive resources of an economy and, therefore, its production possibilities. Investment is at the root of economic growth and development. Investing means giving up consumption in the present in exchange for an increase in capacity production, which will enable greater consumption in the future. Being fundamental for the social well-being of present and future generations, investment is decided, in a market economy, by companies, based on expected profitability. Yours magnitude depends on the interest rate associated with the financing and the expectations of regarding the future economic situation. Approximately 95% of the investment consists of the constitution of physical capital (gross fixed capital), which is the set of physical resources that are used for (buildings, machinery, equipment).