MAT 1339 Lecture Notes - Lecture 1: Differential Calculus, Linear Function
MAT 1339 verified notes
1/27View all
Document Summary
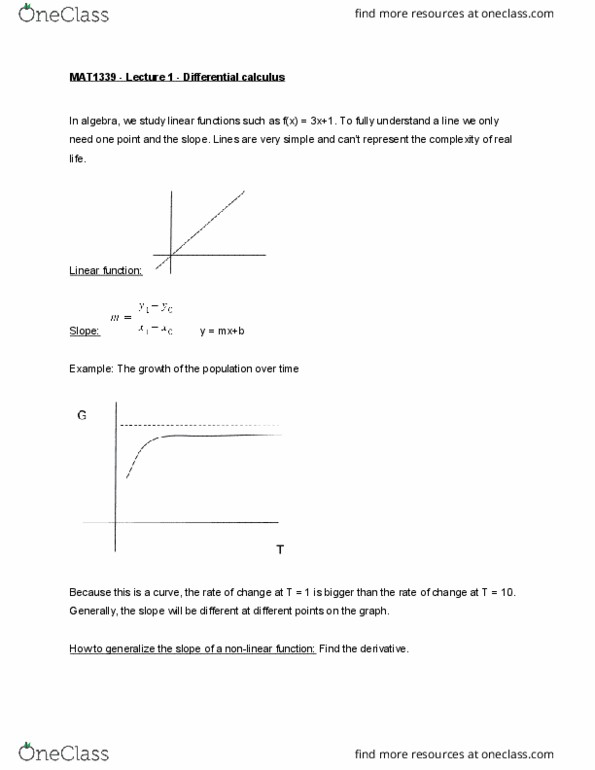
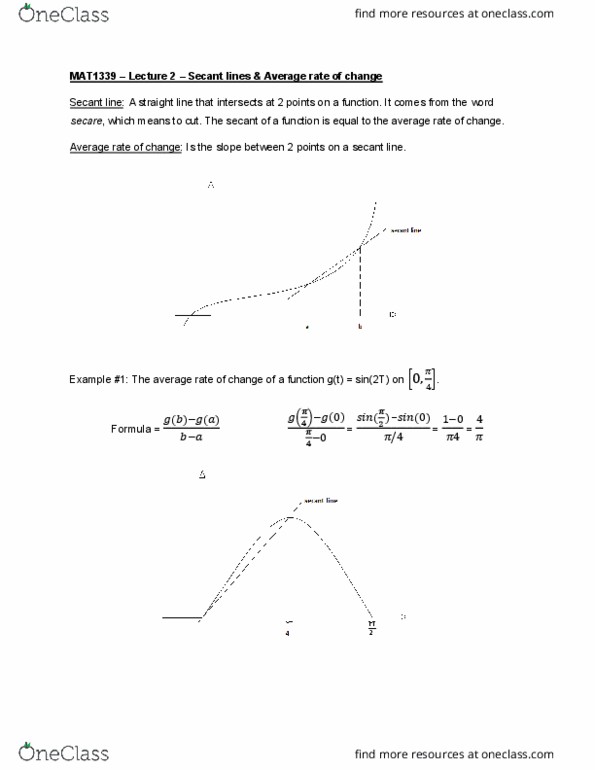
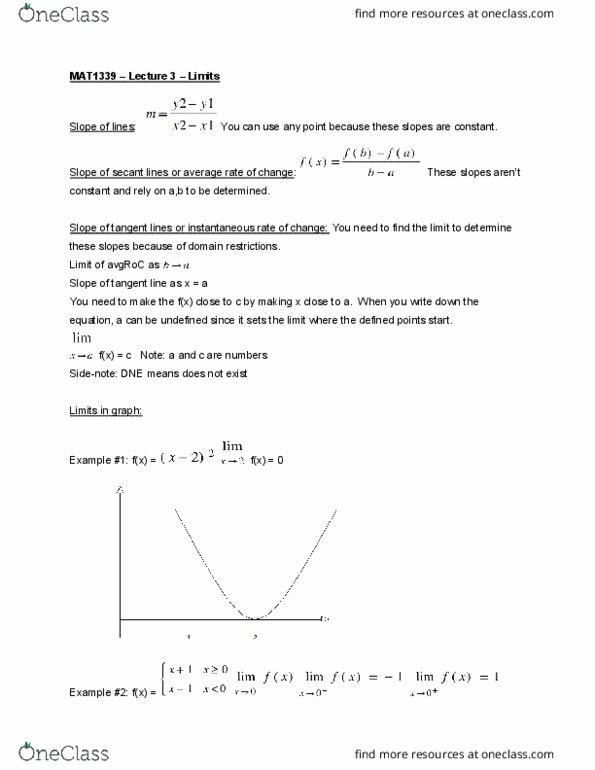
In algebra, we study linear functions such as f(x) = 3x+1. To fully understand a line we only need one point and the slope. Lines are very simple and can"t represent the complexity of real life. Example: the growth of the population over time. Because this is a curve, the rate of change at t = 1 is bigger than the rate of change at t = 10. Generally, the slope will be different at different points on the graph. How to generalize the slope of a non-linear function: find the derivative. We must find the approximation of the slope (rate of change) which is the average rate of change. Example: find the average rate of change of f(x) on. Side-note: a line connecting two points on a graph is called a secant line. This means that the average rate of change of a function on line connecting (a, f(a)) to (b, f(b)).