ECON102 Lecture Notes - Lecture 14: Potential Output, Equilibrium Point, Microsoft Powerpoint
ECON102 verified notes
14/22View all
Document Summary
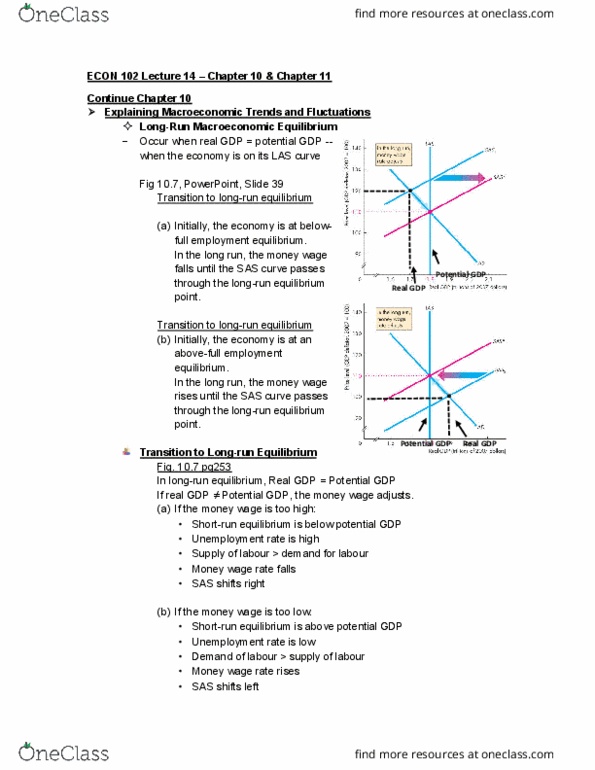
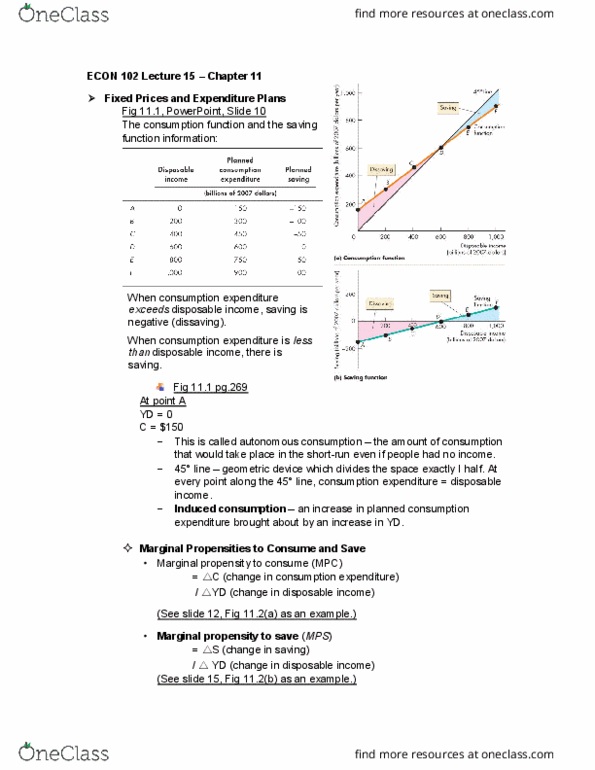
Econ 102 lecture 14 chapter 10 & chapter 11. Occur when real gdp = potential gdp -- when the economy is on its las curve. Transition to long-run equilibrium (a) initially, the economy is at below- full employment equilibrium. In the long run, the money wage falls until the sas curve passes through the long-run equilibrium point. Transition to long-run equilibrium (b) initially, the economy is at an above-full employment equilibrium. In the long run, the money wage rises until the sas curve passes through the long-run equilibrium point. In long-run equilibrium, real gdp = potential gdp. If real gdp potential gdp, the money wage adjusts. (a) if the money wage is too high: Supply of labour > demand for labour. Sas shifts right (b) if the money wage is too low: Demand of labour > supply of labour. An increase in the # of money (shift in ad) in excess of the increase in potential gdp is inflationary.