CISC 102 Lecture Notes - Lecture 35: Logical Consequence, Complex Instruction Set Computing
CISC 102 verified notes
35/38View all
Document Summary
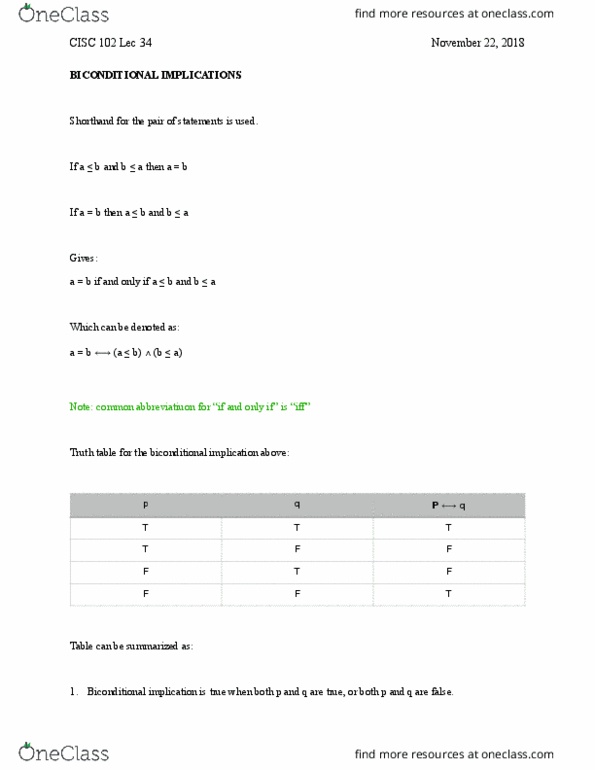
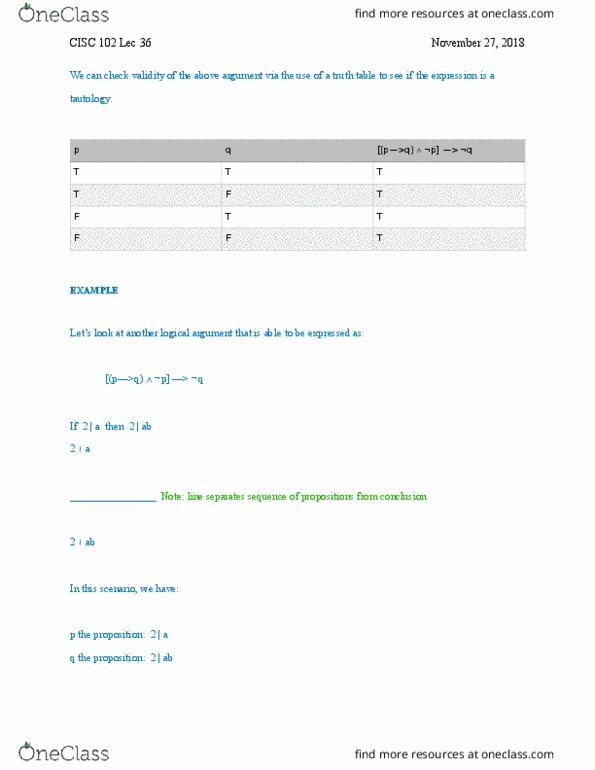
Consider expression below: p is true and p implies q is true, as a consequence we can deduce that q must be true. What one means by a valid argument can be formally defined: the argument p1, p2, p3, , pn q is valid if and only if. P1 p2 p3 pn > q is a tautology. Consider argument below: p > q, q > r, p > r. F (p > q) (q > r) (p > r) [(p > q) (q > r)] > (p > r) If two sides of a triangle are equal, then the opposite angles are equal. T is a triangle w two unequal sides. Conclusion: the opposite angles of t are not equal. Let p be the proposition two sides of a triangle are equal , and let q be the proposition the opposite angles are equal .