ECON 201 Lecture Notes - Lecture 9: Demand Curve, Deadweight Loss, Cost
ECON 201 verified notes
9/25View all
Document Summary
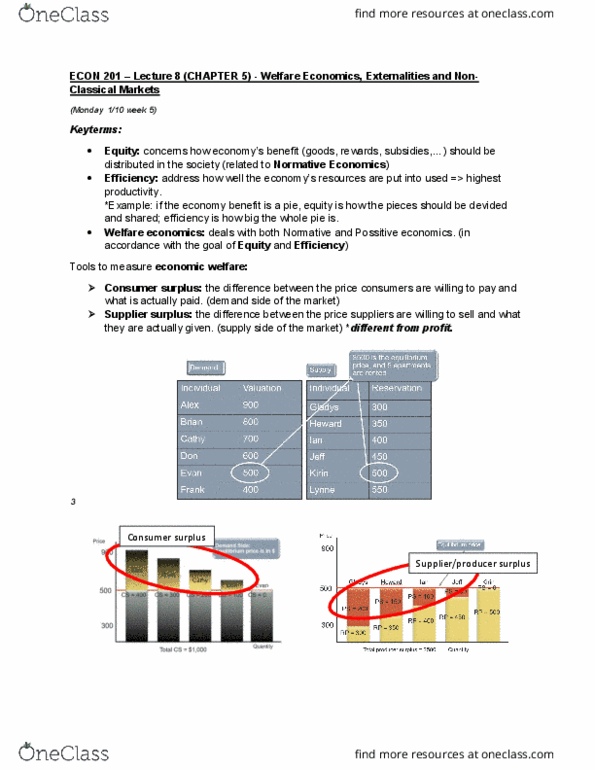
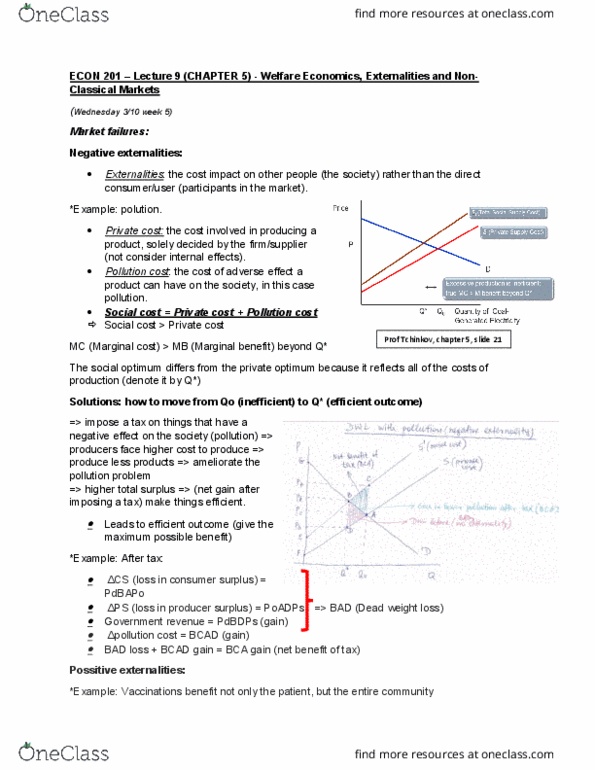
Econ 201 lecture 9 (chapter 5) - welfare economics, externalities and non- Negative externalities: externalities: the cost impact on other people (the society) rather than the direct consumer/user (participants in the market). Mc (marginal cost) > mb (marginal benefit) beyond q* The social optimum differs from the private optimum because it reflects all of the costs of production (denote it by q*) Solutions: how to move from qo (inefficient) to q* (efficient outcome) => impose a tax on things that have a negative effect on the society (pollution) => producers face higher cost to produce => produce less products => ameliorate the pollution problem. => higher total surplus => (net gain after imposing a tax) make things efficient: leads to efficient outcome (give the maximum possible benefit) Ps (loss in producer surplus) = poadps => bad (dead weight loss: government revenue = pdbdps (gain, bad loss + bcad gain = bca gain (net benefit of tax)