CHEM 1A Lecture Notes - Lecture 4: Uncertainty Principle, Louis De Broglie, Photon
CHEM 1A verified notes
4/5View all
Document Summary
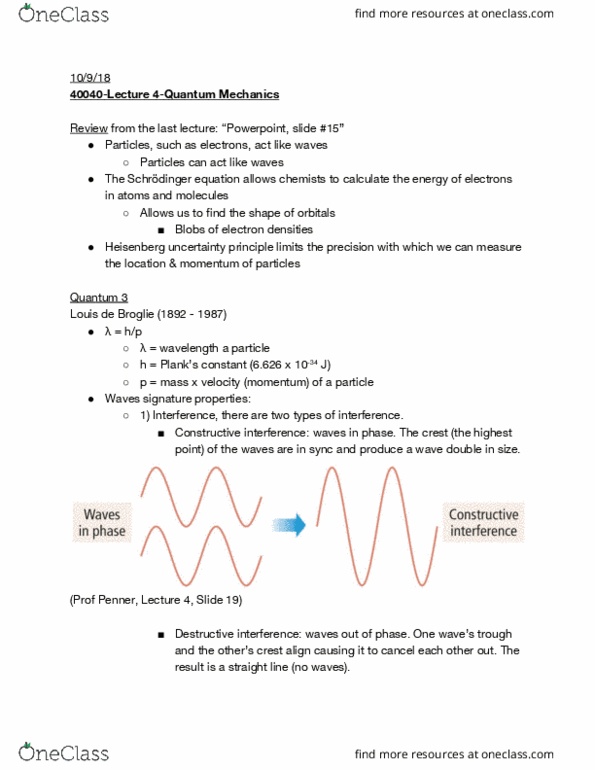
Review from he las lec re: (cid:343)powerpoin , slide #15(cid:344) Particles, such as electrons, act like waves. The schr dinger equation allows chemists to calculate the energy of electrons in atoms and molecules. Allows us to find the shape of orbitals. Heisenberg uncertainty principle limits the precision with which we can measure the location & momentum of particles. H = plank"s cons an (6. 626 x 10-34 j) P = mass x velocity (momentum) of a particle. 1) interference, there are two types of interference. The crest (the highest point) of the waves are in sync and produce a wave double in size. (prof penner, lecture 4, slide 19) One wave"s ro gh and he o her"s cres align ca sing i o cancel each o her o . The result is a straight line (no waves). (prof penner, lecture 4, slide 19) Since a beam of light is a wave, it passes through two small slits.