ECON 2002.01 Lecture 13: Economic Growth (and Inflation)
ECON 2002.01 verified notes
13/29View all
Document Summary
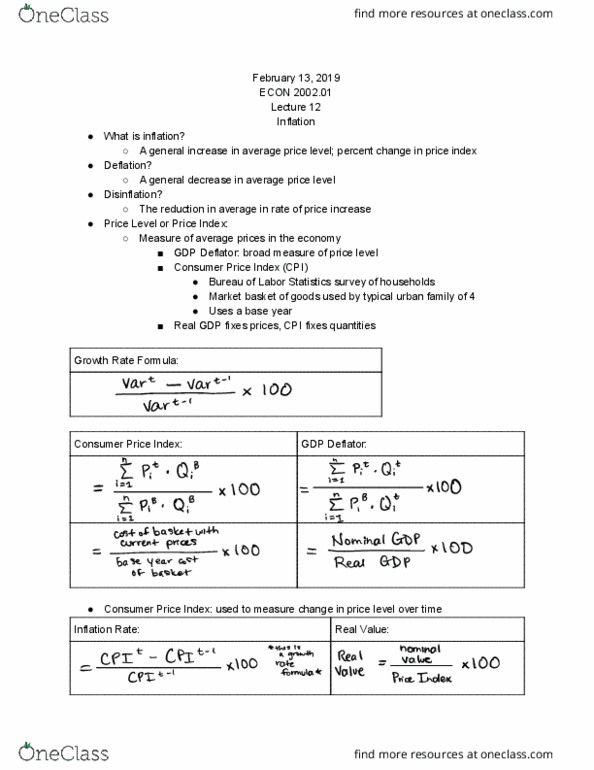
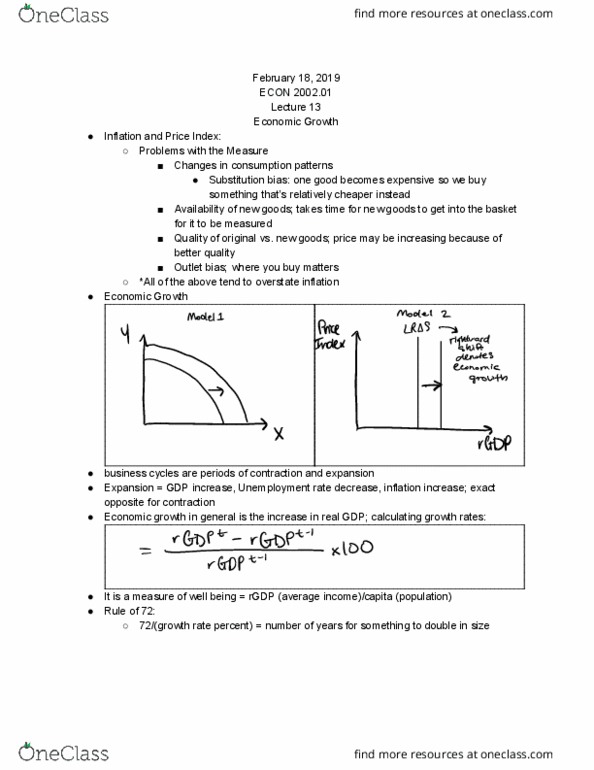
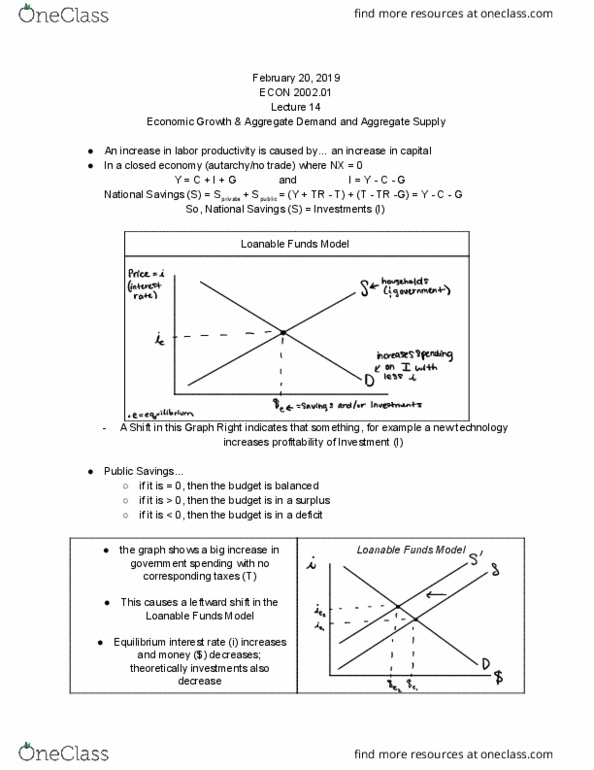
Substitution bias: one good becomes expensive so we buy something that"s relatively cheaper instead. Availability of new goods; takes time for new goods to get into the basket for it to be measured. Quality of original vs. new goods; price may be increasing because of better quality. *all of the above tend to overstate inflation. Business cycles are periods of contraction and expansion. Expansion = gdp increase, unemployment rate decrease, inflation increase; exact opposite for contraction. Economic growth in general is the increase in real gdp; calculating growth rates: It is a measure of well being = rgdp (average income)/capita (population) 72/(growth rate percent) = number of years for something to double in size. Labor productivity is the output produced by 1 unit of labor. Achieved by increase in capital (k)/ unit of labor (l) [k includes human capital] Need a well functioning financial system, 3 sources of funds: Retained earnings = part of profit (pi) that firms keep.