ECON 1011 Lecture Notes - Lecture 24: Price Gouging, Monopsony, Economic Surplus
ECON 1011 verified notes
24/24View all
Document Summary
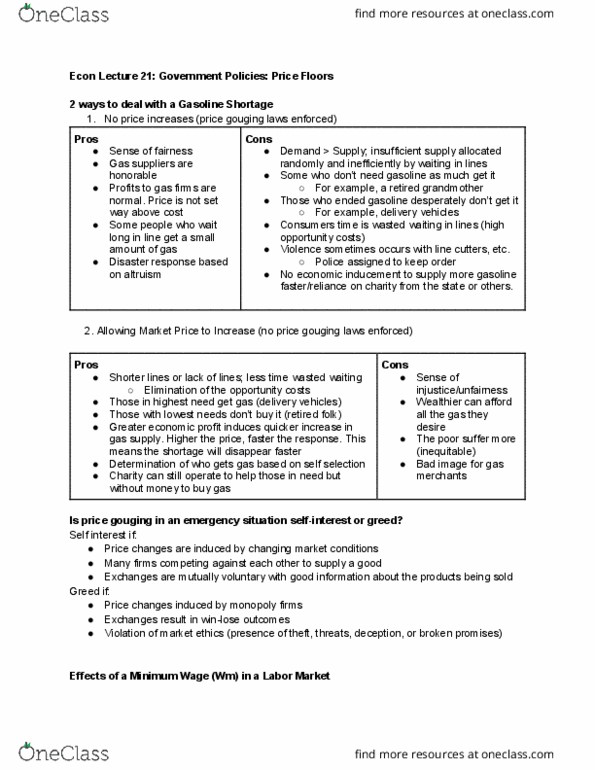
2 ways to deal with a gasoline shortage: no price increases (price gouging laws enforced) Some people who wait long in line get a small amount of gas. Demand > supply; insufficient supply allocated randomly and inefficiently by waiting in lines. Some who don"t need gasoline as much get it. Those who ended gasoline desperately don"t get it. Consumers time is wasted waiting in lines (high opportunity costs) Violence sometimes occurs with line cutters, etc. No economic inducement to supply more gasoline faster/reliance on charity from the state or others. Allowing market price to increase (no price gouging laws enforced) Shorter lines or lack of lines; less time wasted waiting. Those in highest need get gas (delivery vehicles) Those with lowest needs don"t buy it (retired folk) Greater economic profit induces quicker increase in gas supply. Determination of who gets gas based on self selection. Charity can still operate to help those in need but without money to buy gas.