MATH114 Lecture Notes - Lecture 10: Squeeze Theorem, Algebraic Solution, Asymptote
MATH114 verified notes
10/19View all
Document Summary
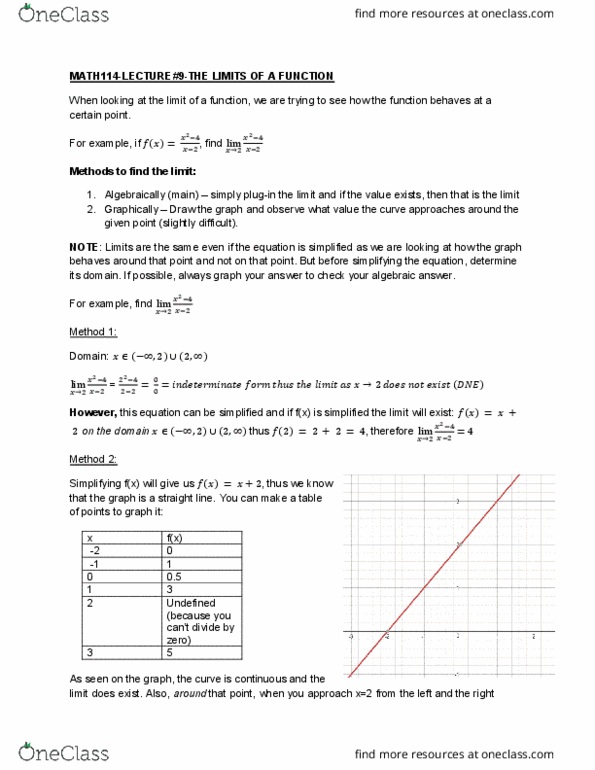
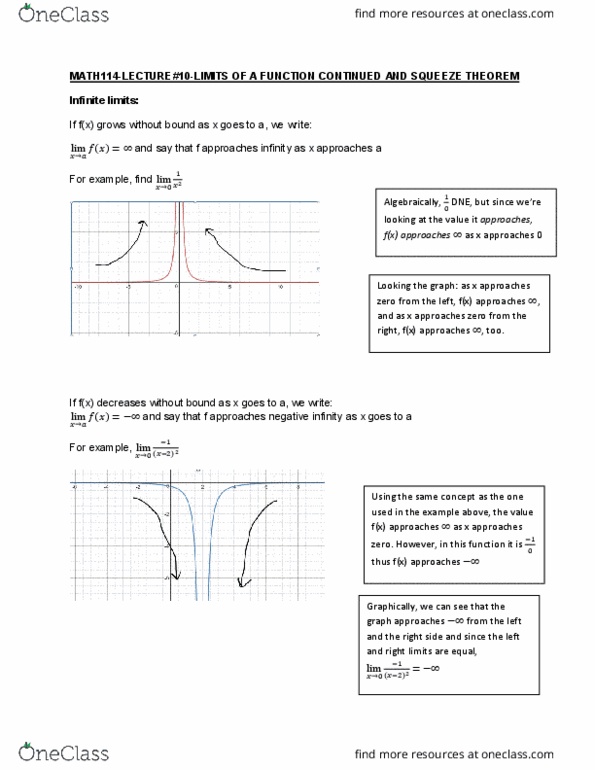
Math114-lecture#10-limits of a function continued and squeeze theorem. If f(x) grows without bound as x goes to a, we write: lim (cid:1858)(cid:4666)(cid:1876)(cid:4667)= and say that f approaches infinity as x approaches a. For example, find lim (cid:2868)(cid:2869)2 looking at the value it approaches, Algebraically, (cid:2869)(cid:2868) dne, (cid:271)ut sin(cid:272)e we"re f(x) approaches as x approaches 0 zero from the left, f(x) approaches , right, f(x) approaches , too. Looking the graph: as x approaches and as x approaches zero from the. If f(x) decreases without bound as x goes to a, we write: lim (cid:1858)(cid:4666)(cid:1876)(cid:4667)= and say that f approaches negative infinity as x goes to a. Using the same concept as the one used in the example above, the value f(x) approaches as x approaches zero. However, in this function it is (cid:2869)(cid:2868) thus f(x) approaches graph approaches from the left lim (cid:2868) (cid:2869) (cid:4666) (cid:2870)(cid:4667)2= and the right side and since the left.