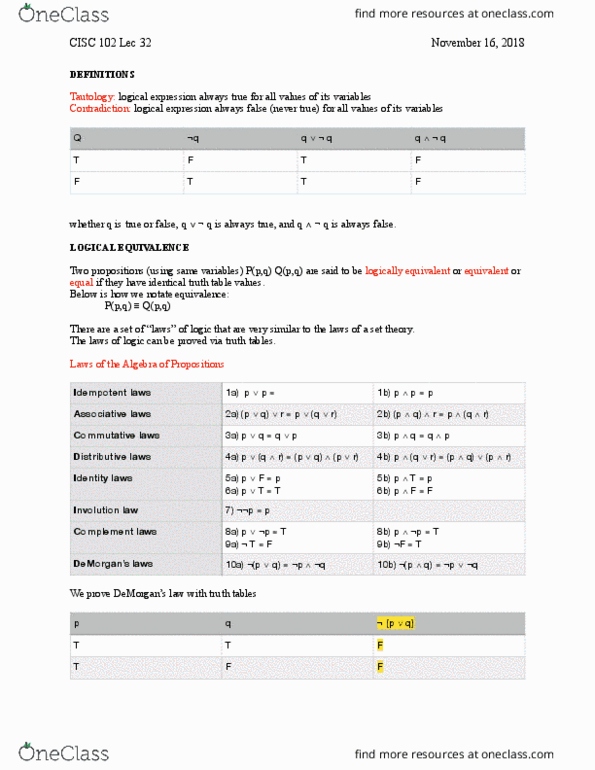
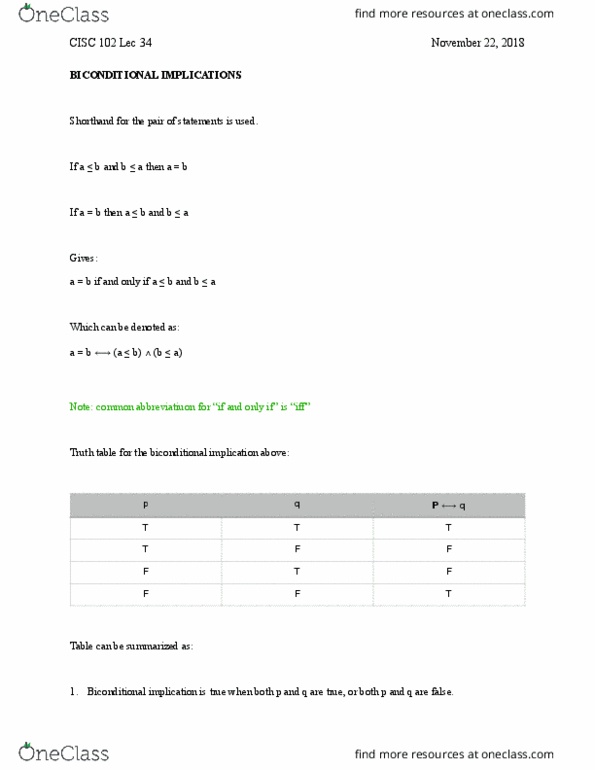
MULTIPLE CHOICE.
1) Which of the following is true of the typical relationship between marginal product (MP) and average product (AP)?
A) The AP curve intersects the MP curve at minimum MP.
B) If MP is less than AP, then AP is increasing.
C) If MP is greater than AP, then AP is falling.
D) The MP curve intersects the AP curve at maximum AP.
TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false.
2) If, for a particular short-run production, we observe that marginal product is decreasing we can conclude that average product is decreasing as well.
MULTIPLE CHOICE.
3) An implicit cost is defined as:
A) the amount by which the money spent on an input to production exceeds its opportunity cost.
B) the difference between an input's explicit cost and its actual cost.
C) the opportunity cost of using a resource that is not explicitly paid out by the firm.
D) the amount by which economic profit exceeds accounting profit.
MULTIPLE CHOICE.
4) The amount of output a firm can produce with a given quantity of fixed and variable inputs is called:
A) total fixed product.
B) average variable product.
C) marginal product.
D) total product.
5) Which of the following statements is true of the relationship among the average cost functions?
A) AFC = ATC + AVC
B) ATC = AFC - AVC
C) AVC = AFC + ATC
D) AFC = ATC - AVC
TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false.
6) A firm's production function is the relationship between the factors of production and the resulting outputs of the production process.
MULTIPLE CHOICE.
Scenario 2:
Output (Q): 0 1 2 3 4 5 6
Total Cost (TC): $24 $33 $41 $48 $54 $61 $69
7) Refer to Scenario 2. Diminishing marginal returns starts to occur between units:
A) 2 and 3.
B) 3 and 4.
C) 4 and 5.
D) 5 and 6.
8) Which of the following would be classified as a short-run decision?
A) trucking firm's decision to move to a smaller facility.
B) A firm's decision to decrease the amount of electricity used in day-to-day operations by encouraging employees to adopt conservation strategies, e.g., shut off lights when leaving a room.
C) A university's decision to add a new residence hall.
D) A restaurant's decision to increase the number of patrons it can accommodate by adding on a new dining room.
9) Economic profit is equal to the difference between: 9)
1.
2.
3.
4.
TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false.
10) At the point where a firm incurs diminishing marginal returns, total product will begin to decline.
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
11) In the context of a production function, the remote order takers in the fast food industry would be classified as:
A) a fixed input.
B) a marginal input.
C) an inframarginal input.
D) a variable input.
Scenario 3:
Total Product (Q): 0 1 2 3 4 5 6
Total Cost (TC): $50 $80 $105 $125 $155 $195 $250
12.
13.
increase; lower
decrease; lower
increase; higher
decrease; higher
TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false.
14.
15.
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
16) A labor-intensive method of production is one that:
A) combines a small but sophisticated labor force with a large amount of capital.
B) requires employees to work harder than they would in other occupations.
C) relies on large quantities of labor and smaller quantities of capital equipment. D) relies exclusively on labor.
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
17) Assume a firm produces 500 units of a good by using two inputs, capital and labor, whose per unit prices are $10 and $4. Assume also that the marginal physical product of the last unit of capital is 30 and the marginal physical product of the last unit of labor is 10. To minimize costs this firm should employ:
A) more labor and less capital. B) more capital and less labor.
C) the existing combination of resources. D) both more labor and more capital.
TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false.
18) All else constant, a decrease in the per unit price of labor would create an incentive for a firm manager to substitute labor for capital in the firm's production process.
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
19) All else constant, as the price of petroleum increases relative to the prices of other inputs to the production process, in their effort to minimize their total costs of production, we can expect to see firms employ:
A) the same amount of petroleum since there are no substitutes for petroleum. B) less petroleum and more of the other inputs to production.
C) less of each of the inputs of production.
D) more petroleum and less of the other inputs to production.