NUR 239 Chapter Notes - Chapter 7: Mycobacterium, Protozoa, Terfenadine

Questions for PGR 7
1. List common illnesses caused by viruses.
o Avian influenza A, herpesvirus infections, human immunodeficiency virus
infection, human papillomavirus, respiratory syncytial virus, viral hepatitis
2. How do viruses gain entry into the host’s cells?
o By binding to receptors on cell membrane
3. How are viral infections spread?
o Secretions from infected people, ingestion of contaminated food or water, breaks
in the skin or mucous membranes, sexual contact, pregnancy, breast-feeding, and organ
transplantation
4. Define the terms: immunocompetence and immunocompromised
o Immunocompetence- An intact immune system.
o Immunocompromised- Impaired or weakened immune system and may develop
the infection because of decreased immunity.
5. Name a viral illness that is chronic-
o Herpesvirus
6. What are the signs and symptoms of an acute viral infection? Are the s/s local or system?
o Fever, headache, cough, malaise, muscle pain, nausea, vomiting diarrhea,
insomnia, and photophobia
7. How do anti-viral drugs work?
o Inhibit viral reproduction but do not eliminate viruses from tissues.
8. Summarize the Patient Teaching Guidelines for Antiviral Drugs (Box 23.2/p.
432).
o Prevention is better than treatment, the medications for viral infections have
serious adverse effects
o Wash hand thoroughly and often
o Have immunuzations against viral infections as indicated
o With genital herpes, avoid sexual intercourse when visible lesions are present and
always wash hands after touching any lesion
o Ask health care provider for information about managing adverse drug effects
o If taking foscarnet or ganciclovir for CMS retinitis have eye examination every 6
weeks
o If taking ganciclovir maintain regular appointments for the assessment of the
complete blood count and renal function
o Administer antiviral agents for recurrent genital herpes lesions as soon as signs
and symptoms begin
o Use gloves to apply topical antiviral ointment to lesions
9. Name the vaccines use to prevent viral illnesses. (look in Frandsen chapter 12)
find more resources at oneclass.com
find more resources at oneclass.com

Table 1 - Chapter 18
Beta-Lactam
Antibacterial
Agents
Ampicillin
(Prototype)
Ampicillin-
sulbactam
Amoxicillin &
clavulanate
Cefazolin
(Prototype)
Imipenem-
cilastatin
(Prototype)
Pharmacokine
tics
Kidneys,
unchanged,
½ life: 1-2 hrs.
IM sites,
diffuses into
bile, blister
and tissue
fluids
Liver, ½ life:
1-1.3 hrs.
Oral, 250-1000 mg
8h or 875 mg every
12
Kidneys,
peak in 1
min-2hrs,
duration 6-12
hr.
Kidneys, rapid
onset, peak at
end of infusion,
duration: 6-8
hrs.
Action Inhibits
bacterial cell
wall synthesis
Bind w/ &
inactivate the
beta-
lactamase
enzymes
Prevent
inactivation of
beta-lactam
antibiotics
Inhibit 3rd and
last step of
bacterial cell
wall
synthesis
Inhibit synthesis
of cell walls
Use Bacterial
infections,
against
infective
endocarditis, in
skin, soft
tissue,
respiratory, GI,
and
genitourinary
infections.
Prophylaxis of
infective
endocarditis
Bacterial
infections
that are
resistant to
beta-lactam
antibiotic
alone
Treatment of skin,
skin structure
infections, otitis
media, sinusitis,
respiratory tract
infections,
genitourinary tract
infections
Surgical
prophylaxis,
parenteral
agent,
treatment of
infections of
respiratory
tract, skin
and soft
tissues, bones
and joints,
urinary tract,
brain and
spinal cord,
and
bloodstream
Infections
caused by orgs
resistant to other
drugs, treat
infections of
lower
respiratory tract,
urinary tract,
intra-abdominal
infections, bone
and joints, and
skin and skin
structures. Treat
polymicrobial
infections,
bacterial
septicemia, and
endocarditis
find more resources at oneclass.com
find more resources at oneclass.com
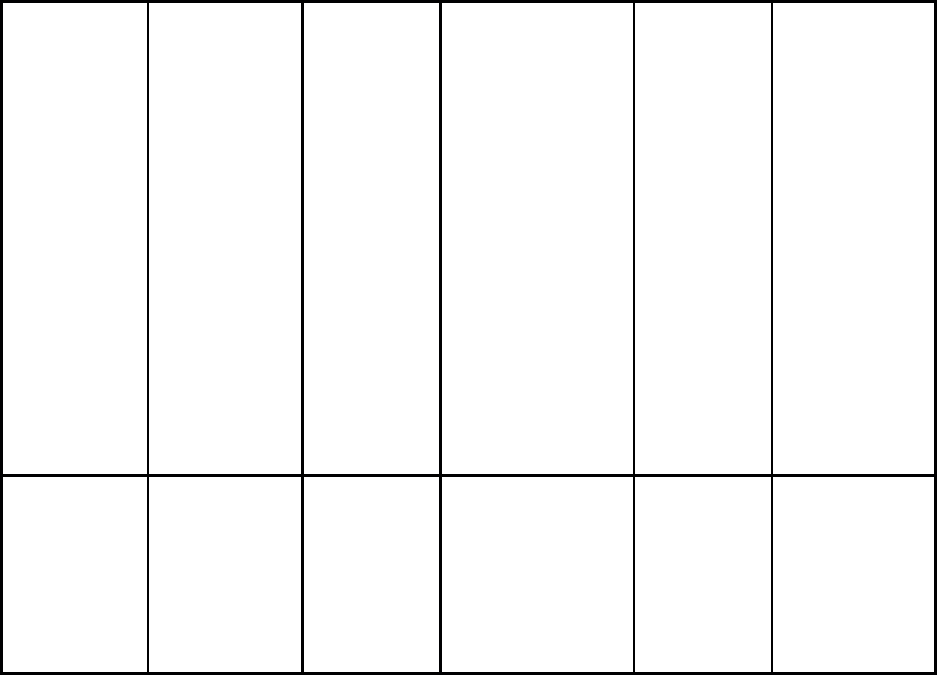
Adverse
Effects
Hypersensitivit
y reactions:
rash/anaphylact
oid reactions”,
diarrhea,
gastritis,
nausea,
vomiting,
interstitial
nephritis,
confusion,
lethargy,
twitching,
dysphagia,
seizures, coma,
hypokalemia,
hypernatremia
Seizures,
hepatotoxicit
y, clostridium
diarrhea,
erythema
multiforme,
Stevens
-Johnson
syndrome,
toxic
epidermal
necrolysis,
anaphylaxis,
serum
sickness
Seizures, diarrhea,
rash, anaphylaxis
and serum sickness
Abdominal
pain,
diarrhea,
gastritis,
nausea,
vomiting.
Hypersensitiv
ity
Cross
sensitivity, cns
toxicity,
seizures
Contraindicati
ons
Hypersensitivit
y to penicillin
Hypersensitiv
ity
Hypersensitivity,
history of
amoxicillin/clavula
nate-associated
cholestatic jaundice
Previous
severe
anaphylactic
reaction to
penicillin,
cephalosporin
allergy.
Hypersensitivity
to carbapenems
find more resources at oneclass.com
find more resources at oneclass.com
Document Summary
Questions for pgr 7: list common illnesses caused by viruses. Avian influenza a, herpesvirus infections, human immunodeficiency virus o infection, human papillomavirus, respiratory syncytial virus, viral hepatitis: how do viruses gain entry into the host"s cells? o. Secretions from infected people, ingestion of contaminated food or water, breaks o in the skin or mucous membranes, sexual contact, pregnancy, breast-feeding, and organ transplantation: define the terms: immunocompetence and immunocompromised. Immunocompromised- impaired or weakened immune system and may develop o o the infection because of decreased immunity: name a viral illness that is chronic- o. Fever, headache, cough, malaise, muscle pain, nausea, vomiting diarrhea, o insomnia, and photophobia: how do anti-viral drugs work? o. Inhibit viral reproduction but do not eliminate viruses from tissues. Summarize the patient teaching guidelines for antiviral drugs (box 23. 2/p. Prevention is better than treatment, the medications for viral infections have.

