PSYC 389 Study Guide - Summer 2018, Comprehensive Midterm Notes - Arousal, Anxiety, Testosterone

PSYC 389
MIDTERM EXAM
STUDY GUIDE
Fall 2018

1
PSYC 389 CH1 Introduction
Why study motivation and emotion
- It’s interesting
- It can help us improve our lives and the lives of others
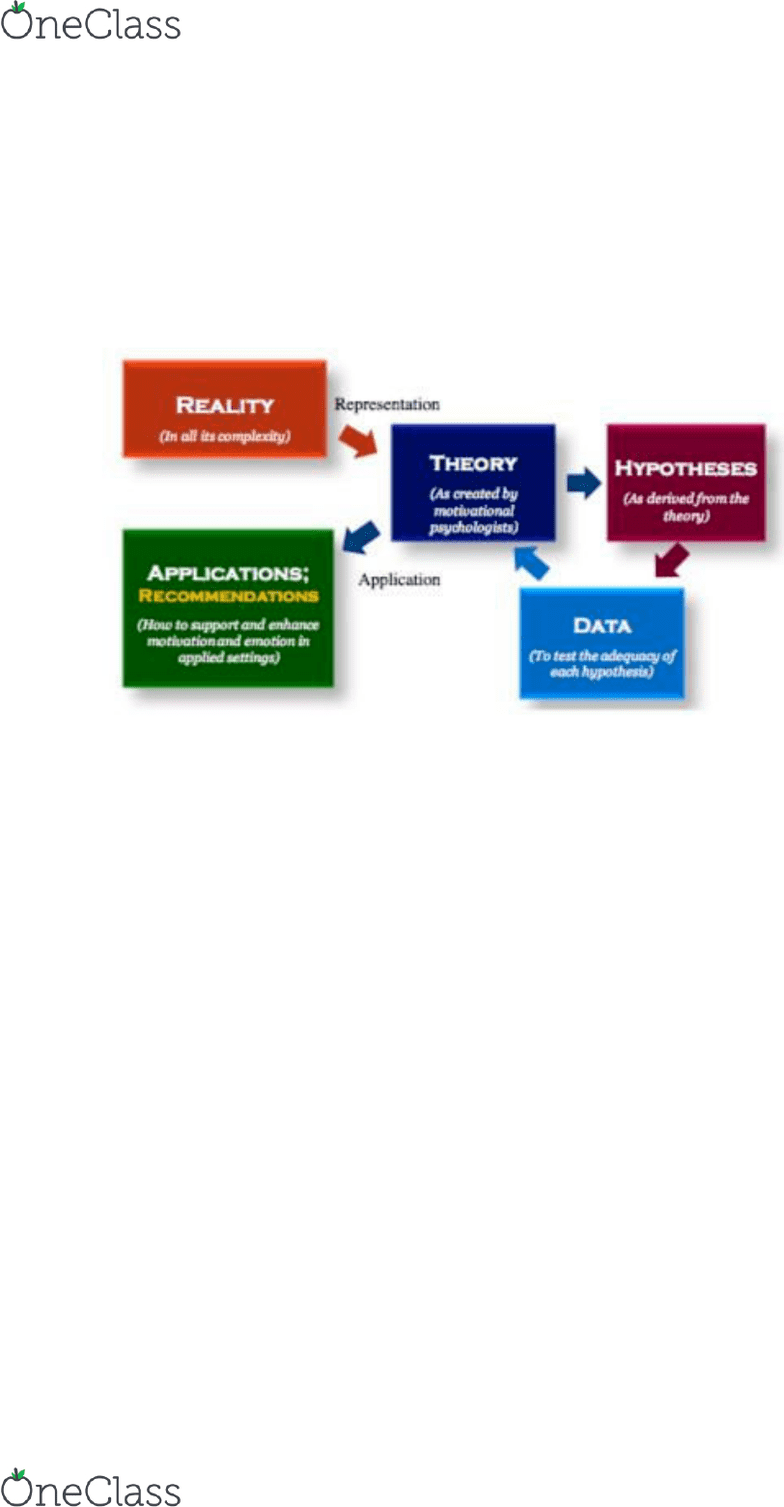
Motivational Science
■ Reality
- Observe how things work in real life
- Children that are rewarded for completing their homework (they are
allowed to watch tv, they are given a snack, they can go outside and play)
stay on task and complete the task, while the other half are not given any
incentive. The researcher measures the amount of time it takes the
children to complete the task and compares these times across the two
groups
■ Theory
- A framework to organize and explain observations
- Providing a clear incentive or reward motivates children to complete their
homework faster than simply instructing them to do the homework
■ Hypothesis
- A prediction about what will happen if the theory is correct
- Children given a clear incentive/ reward will complete homework-like tasks
faster than children not given a clear incentive/ reward
■ Data
- A research study is carried out to collect data to evaluate the hypothesis
find more resources at oneclass.com
find more resources at oneclass.com

2
■ Applications
- Develop ways to apply this knowledge in order to modify the reality
- If the researchers find that incentives and rewards do in fact motivate
children to complete their homework faster, they may develop resources
for parents to help them find appropriate incentives and rewards to use to
motivate their children
Two Perennial questions
1. What causes behavior?
- Motivation exists as a scientific field to identify hidden causes of behavior
- Why does behavior start?
- Once begin, why is behavior sustained over time?
- Why is behavior directed toward some goals yet away from others?
- Why does behavior change its direction?
- Why does behavior stop?
2. Why does behavior vary in its intensity?
- motivation varies both within and between individuals
Motives
- Motives are internal processes that energize, direct and sustain behavior
- Energy: behavior has strength
- Direction: behavior has a purpose
- Persistence: behavior has endurance
- Internal motives: determine behavior
- Needs
- conditions necessary to sustain life, well-being and growth
- Generate wants, desires, and thus motivate behavior
- Eg food, water
- Cognitions
- Mental events: thoughts, beliefs, expectations, plans, foals,
strategies, appraisals, attributions, and the self-concept
- Motivate based on striving to meet expectations, follow through on
plans etc
- Eg only individuals who make 100K a year are successful
- Emotions
find more resources at oneclass.com
find more resources at oneclass.com
