1
answer
0
watching
936
views
11 Dec 2019
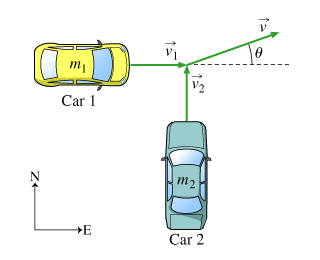
In this problem, let us consider that the two moving objects undergo collision such that after the collision, the objects stick together and travel off as a single unit. This is totally inelastic form of collision.
You are probably familiar that "momentum is conserved" in an inelastic collision. Solve the questions given below to clarify the meaning and implications of "momentum is conserved."
1)What physical quantities are conserved in this type of inelastic collision?
a) the magnitude of the momentum only
b) the net momentum (considered as a vector) only
c) the momentum of each object considered individually
2) Two cars of equal mass collide inelastically and stick together after the collision. Before the collision, their speeds are V1 and V2 . What is the speed of the two-car system after the collision?
a) V1+V2
b) V1-V2
c) V2-V1
d)(V1V2)^(1/2)
e) (1/2)(V1+V2)
f)(V1+V2)^(1/2)
g)The answer depends on the directions in which the cars were moving before the collision.
3) Two cars collide inelastically and stick together after the collision. Before the collision, the magnitudes of their momenta are P1 and P2 . After the collision, what is the magnitude of their combined momentum?
a) P1+P2
b) P1-P2
c) P2-P1
d)(P1P2)^(1/2)
e) (1/2)(P1+P2)
f)(P1+P2)^(1/2)
g)The answer depends on the directions in which the cars were moving before the collision.
4) Two cars collide inelastically and stick together after the collision. Before the collision, their momenta are p1 and p2. After the collision, their combined momentum is vector p. Of what can one be certain?
a) Vector P= p1+p2
b) Vector P= p1-p2
c) Vector P= p2-p1
In this problem, let us consider that the two moving objects undergo collision such that after the collision, the objects stick together and travel off as a single unit. This is totally inelastic form of collision.
You are probably familiar that "momentum is conserved" in an inelastic collision. Solve the questions given below to clarify the meaning and implications of "momentum is conserved."
1)What physical quantities are conserved in this type of inelastic collision?
a) the magnitude of the momentum only
b) the net momentum (considered as a vector) only
c) the momentum of each object considered individually
2) Two cars of equal mass collide inelastically and stick together after the collision. Before the collision, their speeds are V1 and V2 . What is the speed of the two-car system after the collision?
a) V1+V2
b) V1-V2
c) V2-V1
d)(V1V2)^(1/2)
e) (1/2)(V1+V2)
f)(V1+V2)^(1/2)
g)The answer depends on the directions in which the cars were moving before the collision.
3) Two cars collide inelastically and stick together after the collision. Before the collision, the magnitudes of their momenta are P1 and P2 . After the collision, what is the magnitude of their combined momentum?
a) P1+P2
b) P1-P2
c) P2-P1
d)(P1P2)^(1/2)
e) (1/2)(P1+P2)
f)(P1+P2)^(1/2)
g)The answer depends on the directions in which the cars were moving before the collision.
4) Two cars collide inelastically and stick together after the collision. Before the collision, their momenta are p1 and p2. After the collision, their combined momentum is vector p. Of what can one be certain?
a) Vector P= p1+p2
b) Vector P= p1-p2
c) Vector P= p2-p1
You are probably familiar that "momentum is conserved" in an inelastic collision. Solve the questions given below to clarify the meaning and implications of "momentum is conserved."
1)What physical quantities are conserved in this type of inelastic collision?
a) the magnitude of the momentum only
b) the net momentum (considered as a vector) only
c) the momentum of each object considered individually
2) Two cars of equal mass collide inelastically and stick together after the collision. Before the collision, their speeds are V1 and V2 . What is the speed of the two-car system after the collision?
a) V1+V2
b) V1-V2
c) V2-V1
d)(V1V2)^(1/2)
e) (1/2)(V1+V2)
f)(V1+V2)^(1/2)
g)The answer depends on the directions in which the cars were moving before the collision.
3) Two cars collide inelastically and stick together after the collision. Before the collision, the magnitudes of their momenta are P1 and P2 . After the collision, what is the magnitude of their combined momentum?
a) P1+P2
b) P1-P2
c) P2-P1
d)(P1P2)^(1/2)
e) (1/2)(P1+P2)
f)(P1+P2)^(1/2)
g)The answer depends on the directions in which the cars were moving before the collision.
4) Two cars collide inelastically and stick together after the collision. Before the collision, their momenta are p1 and p2. After the collision, their combined momentum is vector p. Of what can one be certain?
a) Vector P= p1+p2
b) Vector P= p1-p2
c) Vector P= p2-p1
Jarrod RobelLv2
29 Feb 2020