BIO101 Lecture Notes - Lecture 2: Symmetry, Nitrogenous Base, Nuclear Dna
NOTES ABOUT DNA(Deoxyribonucleic acid)
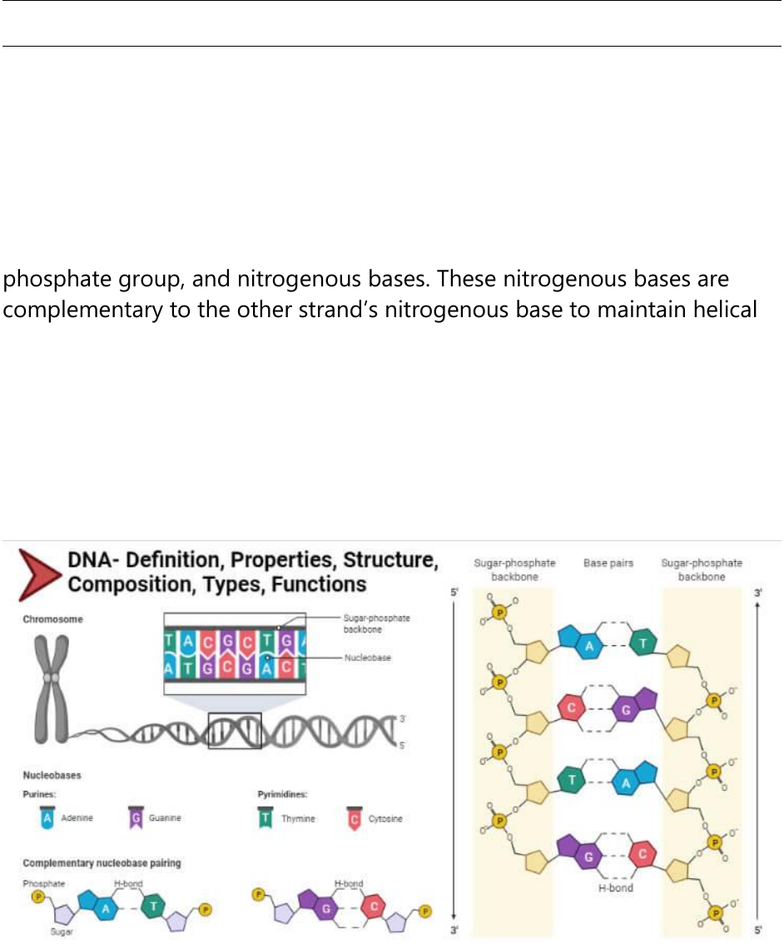
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) Definition
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is the heredity material found in humans and
all living organisms. It is a double-stranded molecule and has a unique
twisted helical structure. DNA is made up of nucleotides, each nucleotide
has three components: a backbone made up of a sugar (Deoxyribose) and
phosphate group and a nitrogen-containing base attached to the
sugar. Each strand has many nucleotides or says numerous sugar, a
phosphate group, and nitrogenous bases. These nitrogenous bases are
complementary to the other strand’s nitrogenous base to maintain helical
symmetry. Each base pairs are bonded through Hydrogen bonding. These
nitrogenous bases are Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Cytosine (C), and Thymine
(T), A is complementary to T, and G to C. These bases are responsible for
storing the genetic information. Most DNA is located at the cell nucleus so
is called nuclear DNA, however, a small amount of DNA is also located in
mitochondria, and so is referred to as mitochondrial DNA.

Properties of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid)
1. DNA is made up of two helical strands that are coiled around the same
axis. If coiled from right it is known as right-handed helices DNA and if
coiled from left then it is known as left-handed helices. However, the
right-handed helices DNA is the most stable and thus the structure of it
is to be referred to as the standard.
2. The two chains of helices run antiparallel to each other. Thus, one strand
runs 5’ to 3’ and another strand runs from 3’ to 5’.
3. Both the strands denature on heating and can renature or say hybridize
on cooling. However, the temperature on which these strands are
separately permanently is referred to as melting temperature and varies
according to the specific sequence of DNA.
4. For instance, the region of higher concentration of C-G has a higher
melting temperature cause these bases are bonded with three hydrogen
bonds, which require more energy to break than the region of higher
concentration A-T which are bonded only with two hydrogen bonds.
5. These nitrogenous bases store genetic information and thus encode for
amino acids which give rise to proteins.
Structure and Composition of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic
acid)
1. DNA is made of two helical chains that intertwine with each other to
form a double helix. The most widely accepted structure of DNA is right-
handed helix DNA also known as the B-form of DNA, which is 1.9 nm in
diameter.
2. These helical chains run anti-parallel to each other, one polynucleotide
chain runs from 5’ to 3’ and the other polynucleotide chain runs from 3’
Document Summary
Deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) is the heredity material found in humans and all living organisms. It is a double-stranded molecule and has a unique twisted helical structure. Dna is made up of nucleotides, each nucleotide has three components: a backbone made up of a sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate group and a nitrogen-containing base attached to the sugar. Each strand has many nucleotides or says numerous sugar, a phosphate group, and nitrogenous bases. These nitrogenous bases are complementary to the other strand"s nitrogenous base to maintain helical symmetry. Each base pairs are bonded through hydrogen bonding. These nitrogenous bases are adenine (a), guanine (g), cytosine (c), and thymine (t), a is complementary to t, and g to c. these bases are responsible for storing the genetic information. Most dna is located at the cell nucleus so is called nuclear dna, however, a small amount of dna is also located in mitochondria, and so is referred to as mitochondrial dna.


