PH 102 Lecture Notes - Lecture 6: Capacitor, Farad, Electric Field
Document Summary
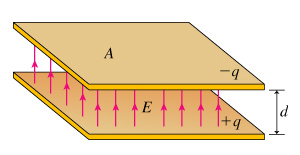
A capacitor consists of two metal electrodes which can be given equal and opposite charges. If the electrodes have charges q and q, then there is an electric field between them which originates on q and terminates on q. There is also a potential difference between the electrodes which is proportional to q. The capacitance of the configuration is defined as. V (unit = c/v = farad = f) The capacitance is a measure of the capacity of the electrodes to hold charge for a given potential difference. A geometrical simple capacitor would consist of two parallel metal plates. If the separation of the plates is small compared with the plate dimensions, then the electric field between the plates is nearly uniform. At the end of chapter 15 we saw that the electric field between two oppositely charged plates is given by e = / 0, where is the charge per unit area ( = q/a) on the plates.