BI110 Lecture Notes - Lecture 22: Glycogen, Starch, Hydrolysis
BI110 Lecture 22 (Monday November 6th)
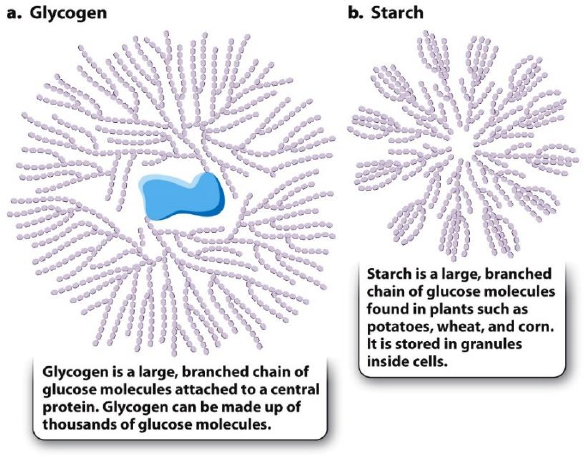
Glucose Storage
• Glycogen has a protein molecule and starch does not
o They are also linked together
differently
• In animal cells, excess glucose is stored
as glycogen
o Glycogen is stored in muscle
cells and liver cells.
▪ since muscle cells need
a lot of ATP
▪ The liver stores
glycogen to be used
throughout the whole
body
▪ Muscle cells store it for
their own personal use
o 1. When stored in muscle cells,
it is used to provide ATP for
muscle contraction.
o 2. The liver stores glycogen for the whole body, releasing it when it is needed elsewhere
o An enzyme will cleave glucose molecules off and send them to glycolysis when needed
• In plants, glucose is stored as starch, another large, branched chain of glucose molecules (ex.
potatoes)
o Starch molecules are so large they from granules (little grains)
How others sugars contribute to glycolysis
• Remember: glucose isn’t the only thing that can be used in glycolysis
• The hydrolysis of some disaccharides produce glucose molecules, that directly enter glycolysis.
o Disaccharides can be cleaved into monosaccharides of glucose for glycolysis
• Monosaccharides can be converted to glycolysis intermediates
o Remember that products of glycolysis can be diverted away and used for other things
o Intermediates of pathway can be produced in other ways and enter pathway mid-
stream
• Monosaccharides, other than glucose, are converted into glycolysis intermediates that come
later in the pathway.
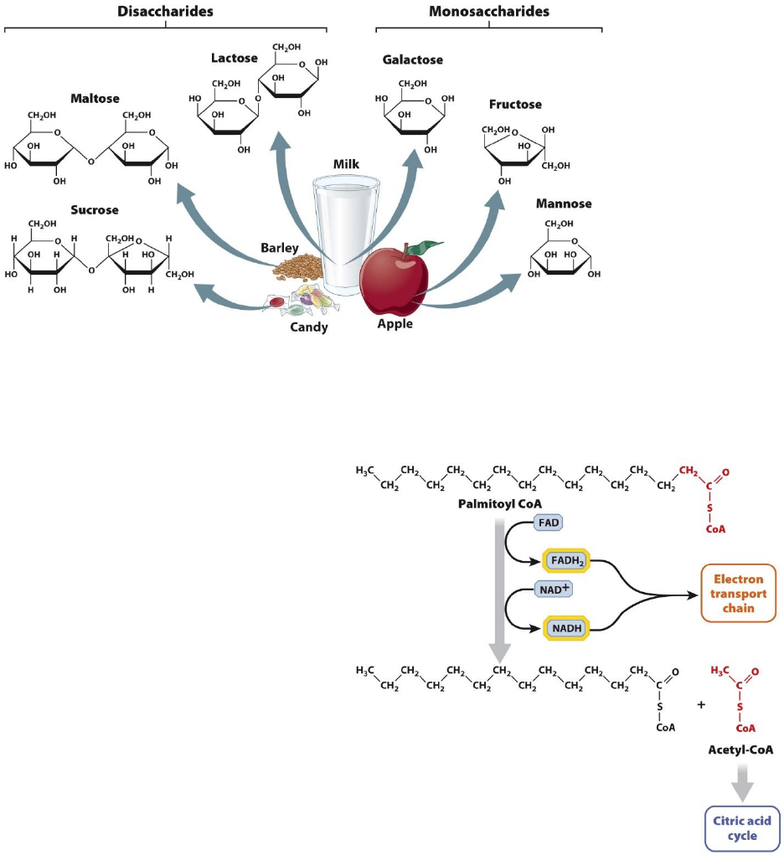
Beta – Oxidation
• Fatty acids can be used for the ETC and citric acid cycle
• Fatty acids are shortened by β-oxidation.
o Break down of a long hydrocarbon chain through a process that produces two carbon
products
o 2 carbons at a time are removed
from the chain to make an acetyl
group, which is then linked to Co-
enzyme A
o Second product is produced from
reduction of FAD and NAD+ to make
FADH2 and NADH
o Does not involve glycolysis, but
produces many products of glycolysis
and pyruvate oxidation
• ATP is not produced directly in βoxidation,
rather electron carriers (NADH and FADH2)
and acetyl-CoA are generated, which feed the
ETC and citric acid cycle.
• Fatty acids produce more energy per unit of
weight compared to glucose

Regulation of cellular respiration
• Amount of energy needed by a cell is constantly
changing, and is different for different types of
cells
o So, cells need a way to provide more ATP
when required, and a way to slow down
production of ATP when not as much is
needed
• How does the cell do it?
o Must monitor energy state of the cell and
respond accordingly
o Can do this by being sensitive to
concentrations of products of the
pathways
▪ High ADP and high NAD+ levels
indicate low energy state in cell
▪ *Amount of ADP is directly
related to amount of ATP
• Same as with NAD+ and
NADH as well as FAD and
FADH2
o Green arrows – pathways getting turned
on
o Red arrows – pathways getting turned off
o High concentrations of ATP and NADH
slows down and inhibits the pathways of
cellular respiration because the cell
already has more than enough ATP
Document Summary
Glucose storage: glycogen has a protein molecule and starch does not, they are also linked together differently. When stored in muscle cells, it is used to provide atp for muscle contraction: 2. The liver stores glycogen for the whole body, releasing it when it is needed elsewhere: an enzyme will cleave glucose molecules off and send them to glycolysis when needed. In plants, glucose is stored as starch, another large, branched chain of glucose molecules (ex. potatoes: starch molecules are so large they from granules (little grains) Intermediates of pathway can be produced in other ways and enter pathway mid- stream: monosaccharides, other than glucose, are converted into glycolysis intermediates that come later in the pathway. Fadh2 and nadh: does not involve glycolysis, but produces many products of glycolysis and pyruvate oxidation, atp is not produced directly in oxidation, rather electron carriers (nadh and fadh2) and acetyl-coa are generated, which feed the.

