Engineering Science 1036A/B Lecture 18: Pointers: Pointers
Pointer: special variable
•
Contains an address of an existing variable
•
Pointer variable is declared with asterisk (*) sign followed by the name of the
variable
Asterisk sign: pointer operator
○
int *ptr
○
•
If an already declared pointer variable uses the * sign in front of it, the * sign is
called as indirection or dereferencing operator
•
Pointer/Dereferencing Operator (*)
When * is used with the data type (double *p), the compiler interprets * as a
pointer operator in pointer declaration
•
When * is used with the name (not data-type) of the pointer only (*p = 10),
the asterisk is interpreted as dereferencing operator
•
Declaring Pointer Variables
General form:
type *name1;
○
type* name1;
○
•
When declaring more than one pointer variable, the * must precede each
variable
type *name1, *name2, *name3;
○
type* name1, *name2, *name3;
○
•
The type is any variable (int, char, etc,) or object (user defined) type
•
The name has to be a valid identifier
•
Example
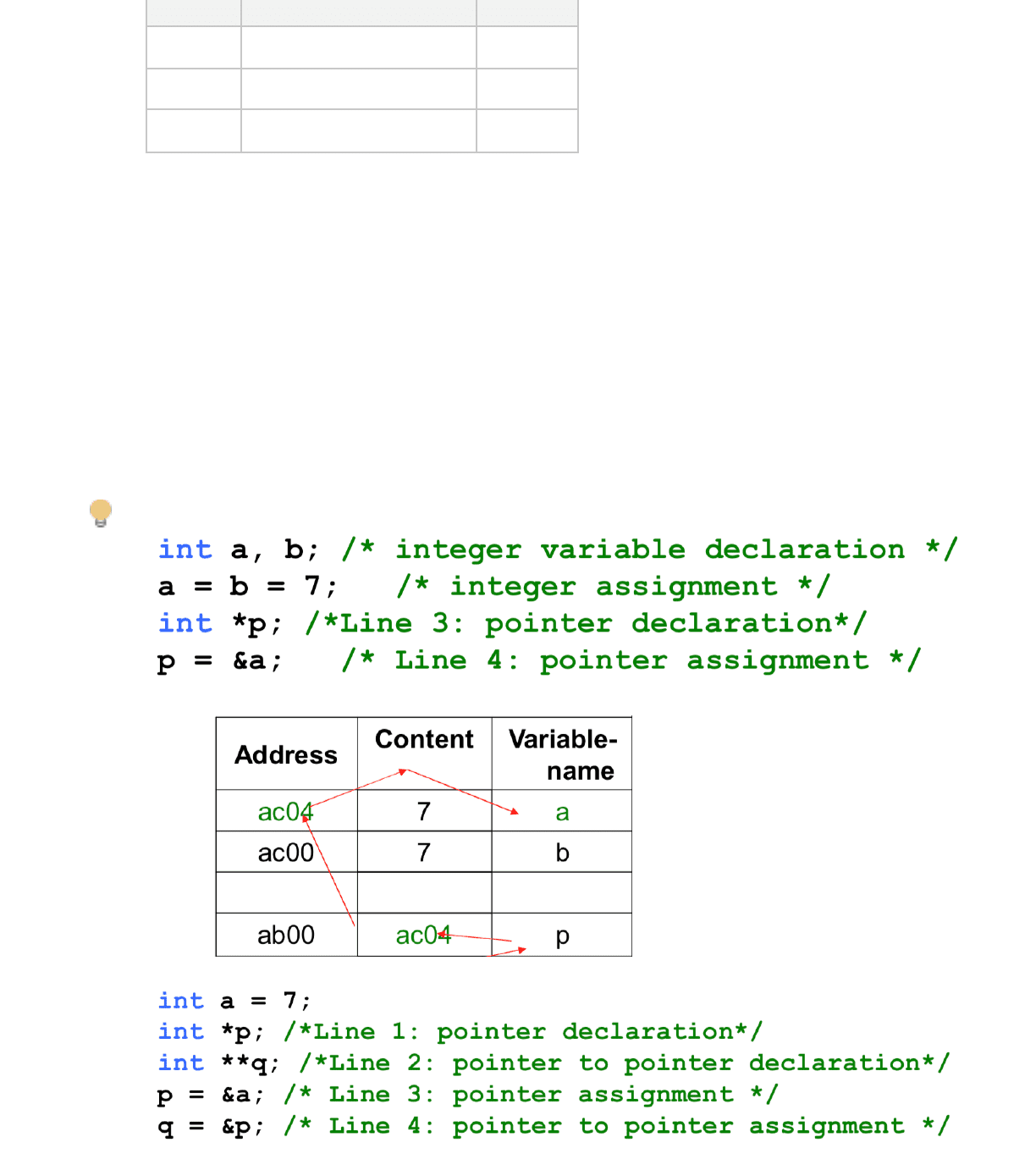
int a,b
Integer variables
○
•
int *p
p is a pointer to an int
○
•
Address
Value
Variable
Ac04 Some integer value a
Ac00 Some integer value b
Ab00 Address of an integer p
Initializing/ Assigning Values to a Pointer Variable
Before using any pointer-variable it has to be initialized with:
An address of an existing variable (which has already been declared) using
the &operator
&: address-of/reference operator
§
○
The address of another existing pointer variable
○
NULL or 0
Assigning NULL or 0 to a pointer indicates that it is not pointing
anywhere
§
It only checks of a pointer has been assigned a value or not
§
○
•
Example
Lines 3 and 4 can be written as: int *p = &a;
○
pis pointing to variable "a" (a's address is held in p)
§
○
•
•
Address-of Operator (&)
The address-of operator in front of any variable produces the address of that
variable
•
Example
int x=75
cout << "x is " << x << endl;
cout << "Address of x is " << & x;
Address Value Variable
002ff50 75 x
x is 75
Address of x (&x) is 002ff50
Dereferencing Pointer Variables
Dereferencing a pointer: accessing a value of a variable using a pointer
Dereferencing operator (*) is used
○
•
Example
Program example: string and character pointers
The Base Type
Base type is the type of variable whose address is held by the pointer
○
•
Since any pointer stores an address (or 0), the size of pointer variables are the
same (4 bytes)
•
A pointer and the variable that the pointer is point to must be of the same type
Other wise it will result in a compilation error
○
○
•
Base type also affects pointer arithmetic•
NULL Pointer
Other than an address of a variable, there is only one value that can be assigned
to any pointer
"NULL" or 0
○
•
Does not point to anything that can be references•
Dereferencing the null address will result in a runtime error
○
•
Program example: srand() and time()
Using non-initialized Pointers
int *iPtr;
*iPtr = 100;
iPtr has not been initialized. The value 100 will be assigned to some
memory location
○
This will result a run-time error (debug error); not compiler error
○
Pointers

Pointer: special variable•
Contains an address of an existing variable•
Pointer variable is declared with asterisk (*) sign followed by the name of the
variable
Asterisk sign: pointer operator
○
int *ptr
○
•
If an already declared pointer variable uses the * sign in front of it, the * sign is
called as indirection or dereferencing operator
•
Pointer/Dereferencing Operator (*)
When * is used with the data type (double *p), the compiler interprets * as a
pointer operator in pointer declaration
•
When * is used with the name (not data-type) of the pointer only (*p = 10),
the asterisk is interpreted as dereferencing operator
•
Declaring Pointer Variables
General form:
type *name1;
○
type* name1;
○
•
When declaring more than one pointer variable, the * must precede each
variable
type *name1, *name2, *name3;
○
type* name1, *name2, *name3;
○
•
The type is any variable (int, char, etc,) or object (user defined) type•
The name has to be a valid identifier•
Example
int a,b
Integer variables
○
•
int *p
p is a pointer to an int
○
•
Address Value Variable
Ac04 Some integer value a
Ac00 Some integer value b
Ab00 Address of an integer p
Initializing/ Assigning Values to a Pointer Variable
Before using any pointer-variable it has to be initialized with:
An address of an existing variable (which has already been declared) using
the &operator
&: address-of/reference operator
§
○
The address of another existing pointer variable
○
NULL or 0
Assigning NULL or 0 to a pointer indicates that it is not pointing
anywhere
§
It only checks of a pointer has been assigned a value or not
§
○
•
Example
Lines 3 and 4 can be written as: int *p = &a;
○
pis pointing to variable "a" (a's address is held in p)
§
○
•
•
Address-of Operator (&)
The address-of operator in front of any variable produces the address of that
variable
•
Example
int x=75
cout << "x is " << x << endl;
cout << "Address of x is " << & x;
Address Value Variable
002ff50 75 x
x is 75
Address of x (&x) is 002ff50
Dereferencing Pointer Variables
Dereferencing a pointer: accessing a value of a variable using a pointer
Dereferencing operator (*) is used
○
•
Example
Program example: string and character pointers
The Base Type
Base type is the type of variable whose address is held by the pointer
○
•
Since any pointer stores an address (or 0), the size of pointer variables are the
same (4 bytes)
•
A pointer and the variable that the pointer is point to must be of the same type
Other wise it will result in a compilation error
○
○
•
Base type also affects pointer arithmetic•
NULL Pointer
Other than an address of a variable, there is only one value that can be assigned
to any pointer
"NULL" or 0
○
•
Does not point to anything that can be references•
Dereferencing the null address will result in a runtime error
○
•
Program example: srand() and time()
Using non-initialized Pointers
int *iPtr;
*iPtr = 100;
iPtr has not been initialized. The value 100 will be assigned to some
memory location
○
This will result a run-time error (debug error); not compiler error
○
Pointers
Pointer: special variable•
Contains an address of an existing variable•
Pointer variable is declared with asterisk (*) sign followed by the name of the
variable
Asterisk sign: pointer operator
○
int *ptr
○
•
If an already declared pointer variable uses the * sign in front of it, the * sign is
called as indirection or dereferencing operator
•
Pointer/Dereferencing Operator (*)
When * is used with the data type (double *p), the compiler interprets * as a
pointer operator in pointer declaration
•
When * is used with the name (not data-type) of the pointer only (*p = 10),
the asterisk is interpreted as dereferencing operator
•
Declaring Pointer Variables
General form:
type *name1;
○
type* name1;
○
•
When declaring more than one pointer variable, the * must precede each
variable
type *name1, *name2, *name3;
○
type* name1, *name2, *name3;
○
•
The type is any variable (int, char, etc,) or object (user defined) type•
The name has to be a valid identifier•
Example
int a,b
Integer variables
○
•
int *p
p is a pointer to an int
○
•
Address
Value
Variable
Ac04
Some integer value
a
Ac00
Some integer value
b
Ab00
Address of an integer
p
Initializing/ Assigning Values to a Pointer Variable
Before using any pointer-variable it has to be initialized with:
An address of an existing variable (which has already been declared) using
the &operator
&: address-of/reference operator
§
○
The address of another existing pointer variable
○
NULL or 0
Assigning NULL or 0 to a pointer indicates that it is not pointing
anywhere
§
It only checks of a pointer has been assigned a value or not
§
○
•
Example
Lines 3 and 4 can be written as: int *p = &a;
○
pis pointing to variable "a" (a's address is held in p)
§
○
•
•
Address-of Operator (&)
The address-of operator in front of any variable produces the address of that
variable
•
Example
int x=75
cout << "x is " << x << endl;
cout << "Address of x is " << & x;
Address Value Variable
002ff50 75 x
x is 75
Address of x (&x) is 002ff50
Dereferencing Pointer Variables
Dereferencing a pointer: accessing a value of a variable using a pointer
Dereferencing operator (*) is used
○
•
Example
Program example: string and character pointers
The Base Type
Base type is the type of variable whose address is held by the pointer
○
•
Since any pointer stores an address (or 0), the size of pointer variables are the
same (4 bytes)
•
A pointer and the variable that the pointer is point to must be of the same type
Other wise it will result in a compilation error
○
○
•
Base type also affects pointer arithmetic•
NULL Pointer
Other than an address of a variable, there is only one value that can be assigned
to any pointer
"NULL" or 0
○
•
Does not point to anything that can be references•
Dereferencing the null address will result in a runtime error
○
•
Program example: srand() and time()
Using non-initialized Pointers
int *iPtr;
*iPtr = 100;
iPtr has not been initialized. The value 100 will be assigned to some
memory location
○
This will result a run-time error (debug error); not compiler error
○
Pointers
Document Summary
Pointer variable is declared with asterisk (*) sign followed by the name of the variable. If an already declared pointer variable uses the * sign in front of it, the * sign is called as indirection or dereferencing operator. When * is used with the data type (double *p), the compiler interprets * as a pointer operator in pointer declaration. When * is used with the name (not data-type) of the pointer only (*p = 10), the asterisk is interpreted as dereferencing operator. When declaring more than one pointer variable, the * must precede each variable type *name1, *name2, *name3; type* name1, *name2, *name3; The type is any variable (int, char, etc,) or object (user defined) type. The name has to be a valid identifier. Integer variables int *p p is a pointer to an int. Before using any pointer-variable it has to be initialized with:

